 @@ -237,4 +237,4 @@ Want to see how it works? Check out the video below:
!!! info "What's next?"
1. See [SSH fleets](../../docs/concepts/fleets.md#ssh-fleets)
2. Read about [dev environments](../../docs/concepts/dev-environments.md), [tasks](../../docs/concepts/tasks.md), and [services](../../docs/concepts/services.md)
- 3. Join [Discord :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://discord.gg/u8SmfwPpMd)
+ 3. Join [Discord](https://discord.gg/u8SmfwPpMd)
diff --git a/docs/blog/posts/benchmark-amd-containers-and-partitions.md b/docs/blog/posts/benchmark-amd-containers-and-partitions.md
index cf1d8baaa..8b945aaba 100644
--- a/docs/blog/posts/benchmark-amd-containers-and-partitions.md
+++ b/docs/blog/posts/benchmark-amd-containers-and-partitions.md
@@ -16,7 +16,7 @@ Our new benchmark explores two important areas for optimizing AI workloads on AM
-This benchmark was supported by [Hot Aisle :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://hotaisle.xyz/){:target="_blank"},
+This benchmark was supported by [Hot Aisle](https://hotaisle.xyz/),
a provider of AMD GPU bare-metal and VM infrastructure.
## Benchmark 1: Bare-metal vs containers
@@ -56,11 +56,11 @@ Our experiments consistently demonstrate that running multi-node AI workloads in
## Benchmark 2: Partition performance isolated vs mesh
-The AMD GPU can be [partitioned :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://instinct.docs.amd.com/projects/amdgpu-docs/en/latest/gpu-partitioning/mi300x/overview.html){:target="_blank"} into smaller, independent units (e.g., NPS4 mode splits one GPU into four partitions). This promises better memory bandwidth utilization. Does this theoretical gain translate to better performance in practice?
+The AMD GPU can be [partitioned](https://instinct.docs.amd.com/projects/amdgpu-docs/en/latest/gpu-partitioning/mi300x/overview.html) into smaller, independent units (e.g., NPS4 mode splits one GPU into four partitions). This promises better memory bandwidth utilization. Does this theoretical gain translate to better performance in practice?
### Finding 1: Higher performance for isolated partitions
-First, we sought to reproduce and extend findings from the [official ROCm blog :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://rocm.blogs.amd.com/software-tools-optimization/compute-memory-modes/README.html){:target="_blank"}. We benchmarked the memory bandwidth of a single partition (in CPX/NPS4 mode) against a full, unpartitioned GPU (in SPX/NPS1 mode).
+First, we sought to reproduce and extend findings from the [official ROCm blog](https://rocm.blogs.amd.com/software-tools-optimization/compute-memory-modes/README.html). We benchmarked the memory bandwidth of a single partition (in CPX/NPS4 mode) against a full, unpartitioned GPU (in SPX/NPS1 mode).
@@ -237,4 +237,4 @@ Want to see how it works? Check out the video below:
!!! info "What's next?"
1. See [SSH fleets](../../docs/concepts/fleets.md#ssh-fleets)
2. Read about [dev environments](../../docs/concepts/dev-environments.md), [tasks](../../docs/concepts/tasks.md), and [services](../../docs/concepts/services.md)
- 3. Join [Discord :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://discord.gg/u8SmfwPpMd)
+ 3. Join [Discord](https://discord.gg/u8SmfwPpMd)
diff --git a/docs/blog/posts/benchmark-amd-containers-and-partitions.md b/docs/blog/posts/benchmark-amd-containers-and-partitions.md
index cf1d8baaa..8b945aaba 100644
--- a/docs/blog/posts/benchmark-amd-containers-and-partitions.md
+++ b/docs/blog/posts/benchmark-amd-containers-and-partitions.md
@@ -16,7 +16,7 @@ Our new benchmark explores two important areas for optimizing AI workloads on AM
-This benchmark was supported by [Hot Aisle :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://hotaisle.xyz/){:target="_blank"},
+This benchmark was supported by [Hot Aisle](https://hotaisle.xyz/),
a provider of AMD GPU bare-metal and VM infrastructure.
## Benchmark 1: Bare-metal vs containers
@@ -56,11 +56,11 @@ Our experiments consistently demonstrate that running multi-node AI workloads in
## Benchmark 2: Partition performance isolated vs mesh
-The AMD GPU can be [partitioned :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://instinct.docs.amd.com/projects/amdgpu-docs/en/latest/gpu-partitioning/mi300x/overview.html){:target="_blank"} into smaller, independent units (e.g., NPS4 mode splits one GPU into four partitions). This promises better memory bandwidth utilization. Does this theoretical gain translate to better performance in practice?
+The AMD GPU can be [partitioned](https://instinct.docs.amd.com/projects/amdgpu-docs/en/latest/gpu-partitioning/mi300x/overview.html) into smaller, independent units (e.g., NPS4 mode splits one GPU into four partitions). This promises better memory bandwidth utilization. Does this theoretical gain translate to better performance in practice?
### Finding 1: Higher performance for isolated partitions
-First, we sought to reproduce and extend findings from the [official ROCm blog :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://rocm.blogs.amd.com/software-tools-optimization/compute-memory-modes/README.html){:target="_blank"}. We benchmarked the memory bandwidth of a single partition (in CPX/NPS4 mode) against a full, unpartitioned GPU (in SPX/NPS1 mode).
+First, we sought to reproduce and extend findings from the [official ROCm blog](https://rocm.blogs.amd.com/software-tools-optimization/compute-memory-modes/README.html). We benchmarked the memory bandwidth of a single partition (in CPX/NPS4 mode) against a full, unpartitioned GPU (in SPX/NPS1 mode).
 @@ -100,7 +100,7 @@ GPU partitioning is only practical if used dynamically—for instance, to run mu
#### Limitations
1. **Reproducibility**: AMD’s original blog post on partitioning lacked detailed setup information, so we had to reconstruct the benchmarks independently.
-2. **Network tuning**: These benchmarks were run on a default, out-of-the-box network configuration. Our results for RCCL (~339 GB/s) and RDMA (~726 Gbps) are slightly below the peak figures [reported by Dell :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://infohub.delltechnologies.com/en-us/l/generative-ai-in-the-enterprise-with-amd-accelerators/rccl-and-perftest-for-cluster-validation-1/4/){:target="_blank"}. This suggests that further performance could be unlocked with expert tuning of network topology, MTU size, and NCCL environment variables.
+2. **Network tuning**: These benchmarks were run on a default, out-of-the-box network configuration. Our results for RCCL (~339 GB/s) and RDMA (~726 Gbps) are slightly below the peak figures [reported by Dell](https://infohub.delltechnologies.com/en-us/l/generative-ai-in-the-enterprise-with-amd-accelerators/rccl-and-perftest-for-cluster-validation-1/4/). This suggests that further performance could be unlocked with expert tuning of network topology, MTU size, and NCCL environment variables.
## Benchmark setup
@@ -352,7 +352,7 @@ The `SIZE` value is `1M`, `2M`, .., `8G`.
**vLLM data parallel**
-1. Build nginx container (see [vLLM-nginx :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://docs.vllm.ai/en/stable/deployment/nginx.html#build-nginx-container){:target="_blank"}).
+1. Build nginx container (see [vLLM-nginx](https://docs.vllm.ai/en/stable/deployment/nginx.html#build-nginx-container)).
2. Create `nginx.conf`
@@ -471,13 +471,13 @@ HIP_VISIBLE_DEVICES=0 python3 toy_inference_benchmark.py \
## Source code
-All source code and findings are available in [our GitHub repo :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://github.com/dstackai/benchmarks/tree/main/amd/baremetal_container_partition){:target="_blank"}.
+All source code and findings are available in [our GitHub repo](https://github.com/dstackai/benchmarks/tree/main/amd/baremetal_container_partition).
## References
-* [AMD Instinct MI300X GPU partitioning overview :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://instinct.docs.amd.com/projects/amdgpu-docs/en/latest/gpu-partitioning/mi300x/overview.html){:target="_blank"}
-* [Deep dive into partition modes by AMD :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://rocm.blogs.amd.com/software-tools-optimization/compute-memory-modes/README.html){:target="_blank"}.
-* [RCCL and PerfTest for cluster validation by Dell :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://infohub.delltechnologies.com/en-us/l/generative-ai-in-the-enterprise-with-amd-accelerators/rccl-and-perftest-for-cluster-validation-1/4/){:target="_blank"}.
+* [AMD Instinct MI300X GPU partitioning overview](https://instinct.docs.amd.com/projects/amdgpu-docs/en/latest/gpu-partitioning/mi300x/overview.html)
+* [Deep dive into partition modes by AMD](https://rocm.blogs.amd.com/software-tools-optimization/compute-memory-modes/README.html).
+* [RCCL and PerfTest for cluster validation by Dell](https://infohub.delltechnologies.com/en-us/l/generative-ai-in-the-enterprise-with-amd-accelerators/rccl-and-perftest-for-cluster-validation-1/4/).
## What's next?
@@ -487,5 +487,5 @@ Benchmark the performance impact of VMs vs bare-metal for inference and training
#### Hot Aisle
-Big thanks to [Hot Aisle :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://hotaisle.xyz/){:target="_blank"} for providing the compute power behind these benchmarks.
+Big thanks to [Hot Aisle](https://hotaisle.xyz/) for providing the compute power behind these benchmarks.
If you’re looking for fast AMD GPU bare-metal or VM instances, they’re definitely worth checking out.
diff --git a/docs/blog/posts/benchmark-amd-vms.md b/docs/blog/posts/benchmark-amd-vms.md
index 099fee9be..b8d9105d0 100644
--- a/docs/blog/posts/benchmark-amd-vms.md
+++ b/docs/blog/posts/benchmark-amd-vms.md
@@ -18,7 +18,7 @@ This is the first in our series of benchmarks exploring the performance of AMD G
Our findings reveal that for single-GPU LLM training and inference, both setups deliver comparable performance. The subtle differences we observed highlight how virtualization overhead can influence performance under specific conditions, but for most practical purposes, the performance is nearly identical.
-This benchmark was supported by [Hot Aisle :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://hotaisle.xyz/){:target="_blank"},
+This benchmark was supported by [Hot Aisle](https://hotaisle.xyz/),
a provider of AMD GPU bare-metal and VM infrastructure.
## Benchmark 1: Inference
@@ -201,11 +201,11 @@ python3 trl/scripts/sft.py \
## Source code
-All source code and findings are available in our [GitHub repo :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://github.com/dstackai/benchmarks/tree/main/amd/single_gpu_vm_vs_bare-metal){:target="_blank"}.
+All source code and findings are available in our [GitHub repo](https://github.com/dstackai/benchmarks/tree/main/amd/single_gpu_vm_vs_bare-metal).
## References
-* [vLLM V1 Meets AMD Instinct GPUs: A New Era for LLM Inference Performance :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://rocm.blogs.amd.com/software-tools-optimization/vllmv1-rocm-llm/README.html){:target="_blank"}
+* [vLLM V1 Meets AMD Instinct GPUs: A New Era for LLM Inference Performance](https://rocm.blogs.amd.com/software-tools-optimization/vllmv1-rocm-llm/README.html)
## What's next?
@@ -215,5 +215,5 @@ Our next steps are to benchmark VM vs. bare-metal performance in multi-GPU and m
#### Hot Aisle
-Big thanks to [Hot Aisle :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://hotaisle.xyz/){:target="_blank"} for providing the compute power behind these benchmarks.
+Big thanks to [Hot Aisle](https://hotaisle.xyz/) for providing the compute power behind these benchmarks.
If you’re looking for fast AMD GPU bare-metal or VM instances, they’re definitely worth checking out.
diff --git a/docs/blog/posts/benchmarking-pd-ratios.md b/docs/blog/posts/benchmarking-pd-ratios.md
index 1069c5794..c303163e1 100644
--- a/docs/blog/posts/benchmarking-pd-ratios.md
+++ b/docs/blog/posts/benchmarking-pd-ratios.md
@@ -21,19 +21,19 @@ We evaluate different ratios across workload profiles and concurrency levels to
### What is Prefill–Decode disaggregation?
-LLM inference has two distinct phases: prefill and decode. Prefill processes all prompt tokens in parallel and is compute-intensive. Decode generates tokens one by one, repeatedly accessing the KV-cache, making it memory- and bandwidth-intensive. DistServe ([Zhong et al., 2024 :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://arxiv.org/pdf/2401.09670){:target="_blank"}) introduced prefill–decode disaggregation to separate these phases across dedicated workers, reducing interference and enabling hardware to be allocated more efficiently.
+LLM inference has two distinct phases: prefill and decode. Prefill processes all prompt tokens in parallel and is compute-intensive. Decode generates tokens one by one, repeatedly accessing the KV-cache, making it memory- and bandwidth-intensive. DistServe ([Zhong et al., 2024](https://arxiv.org/pdf/2401.09670)) introduced prefill–decode disaggregation to separate these phases across dedicated workers, reducing interference and enabling hardware to be allocated more efficiently.
### What is the prefill–decode ratio?
The ratio of prefill to decode workers determines how much capacity is dedicated to each phase. DistServe showed that for a workload with ISL=512 and OSL=64, a 2:1 ratio met both TTFT and TPOT targets. But this example does not answer how the ratio should be chosen more generally, or whether it needs to change at runtime.
!!! info "Reasoning model example"
- In the DeepSeek deployment ([LMSYS, 2025 :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://lmsys.org/blog/2025-05-05-large-scale-ep){:target="_blank"}), the ratio was 1:3. This decode-leaning split reflects reasoning workloads, where long outputs dominate. Allocating more workers to decode reduces inter-token latency and keeps responses streaming smoothly.
+ In the DeepSeek deployment ([LMSYS, 2025](https://lmsys.org/blog/2025-05-05-large-scale-ep)), the ratio was 1:3. This decode-leaning split reflects reasoning workloads, where long outputs dominate. Allocating more workers to decode reduces inter-token latency and keeps responses streaming smoothly.
### Dynamic ratio
-Dynamic approaches, such as NVIDIA’s [SLA-based :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://docs.nvidia.com/dynamo/latest/architecture/sla_planner.html){:target="_blank"}
-and [Load-based :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://docs.nvidia.com/dynamo/latest/architecture/load_planner.html){:target="_blank"} planners, adjust the ratio at runtime according to SLO targets or load. However, they do this in conjunction with auto-scaling, which increases orchestration complexity. This raises the question: does the prefill–decode ratio really need to be dynamic, or can a fixed ratio be chosen ahead of time and still provide robust performance?
+Dynamic approaches, such as NVIDIA’s [SLA-based](https://docs.nvidia.com/dynamo/latest/architecture/sla_planner.html)
+and [Load-based](https://docs.nvidia.com/dynamo/latest/architecture/load_planner.html) planners, adjust the ratio at runtime according to SLO targets or load. However, they do this in conjunction with auto-scaling, which increases orchestration complexity. This raises the question: does the prefill–decode ratio really need to be dynamic, or can a fixed ratio be chosen ahead of time and still provide robust performance?
## Benchmark purpose
@@ -72,7 +72,7 @@ If a fixed ratio consistently performs well across these metrics, it would indic
* **Model**: `openai/gpt-oss-120b`
* **Backend**: SGLang
-For full steps and raw data, see the [GitHub repo :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://github.com/dstackai/benchmarks/tree/main/comparison/pd_ratio){:target="_blank"}.
+For full steps and raw data, see the [GitHub repo](https://github.com/dstackai/benchmarks/tree/main/comparison/pd_ratio).
## Finding 1: Prefill-heavy workloads
@@ -134,8 +134,8 @@ Overall, more study on how the optimal ratio is found and what factors it depend
## References
-* [DistServe :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://arxiv.org/pdf/2401.09670){:target="_blank"}
-* [DeepSeek deployment on 96 H100 GPUs :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://lmsys.org/blog/2025-05-05-large-scale-ep/){:target="_blank"}
-* [Dynamo disaggregated serving :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://docs.nvidia.com/dynamo/latest/architecture/disagg_serving.html#){:target="_blank"}
-* [SGLang PD disaggregation :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://docs.sglang.ai/advanced_features/pd_disaggregation.html){:target="_blank"}
-* [vLLM disaggregated prefilling :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://docs.vllm.ai/en/v0.9.2/features/disagg_prefill.html){:target="_blank"}
+* [DistServe](https://arxiv.org/pdf/2401.09670)
+* [DeepSeek deployment on 96 H100 GPUs](https://lmsys.org/blog/2025-05-05-large-scale-ep/)
+* [Dynamo disaggregated serving](https://docs.nvidia.com/dynamo/latest/architecture/disagg_serving.html#)
+* [SGLang PD disaggregation](https://docs.sglang.ai/advanced_features/pd_disaggregation.html)
+* [vLLM disaggregated prefilling](https://docs.vllm.ai/en/v0.9.2/features/disagg_prefill.html)
diff --git a/docs/blog/posts/beyond-kubernetes-2024-recap-and-whats-ahead.md b/docs/blog/posts/beyond-kubernetes-2024-recap-and-whats-ahead.md
index dec4945ed..4c6b43f9b 100644
--- a/docs/blog/posts/beyond-kubernetes-2024-recap-and-whats-ahead.md
+++ b/docs/blog/posts/beyond-kubernetes-2024-recap-and-whats-ahead.md
@@ -21,25 +21,25 @@ As 2024 comes to a close, we reflect on the milestones we've achieved and look a
While `dstack` integrates with leading cloud GPU providers, we aim to expand partnerships with more providers
sharing our vision of simplifying AI infrastructure orchestration with a lightweight, efficient alternative to Kubernetes.
-This year, we’re excited to welcome our first partners: [Lambda :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://lambdalabs.com/){:target="_blank"},
-[RunPod :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://www.runpod.io/){:target="_blank"},
-[CUDO Compute :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://www.cudocompute.com/){:target="_blank"},
-and [Hot Aisle :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://hotaisle.xyz/){:target="_blank"}.
+This year, we’re excited to welcome our first partners: [Lambda](https://lambdalabs.com/),
+[RunPod](https://www.runpod.io/),
+[CUDO Compute](https://www.cudocompute.com/),
+and [Hot Aisle](https://hotaisle.xyz/).
-We’d also like to thank [Oracle :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://www.oracle.com/cloud/){:target="_blank"}
+We’d also like to thank [Oracle ](https://www.oracle.com/cloud/)
for their collaboration, ensuring seamless integration between `dstack` and OCI.
-> Special thanks to [Lambda :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://lambdalabs.com/){:target="_blank"} and
-> [Hot Aisle :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://hotaisle.xyz/){:target="_blank"} for providing NVIDIA and AMD hardware, enabling us conducting
+> Special thanks to [Lambda](https://lambdalabs.com/) and
+> [Hot Aisle](https://hotaisle.xyz/) for providing NVIDIA and AMD hardware, enabling us conducting
> [benchmarks](/blog/category/benchmarks/), which
> are essential to advancing open-source inference and training stacks for all accelerator chips.
## Community
Thanks to your support, the project has
-reached [1.6K stars on GitHub :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://github.com/dstackai/dstack){:target="_blank"},
+reached [1.6K stars on GitHub](https://github.com/dstackai/dstack),
reflecting the growing interest and trust in its mission.
-Your issues, pull requests, as well as feedback on [Discord :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://discord.gg/u8SmfwPpMd){:target="_blank"}, play a
+Your issues, pull requests, as well as feedback on [Discord](https://discord.gg/u8SmfwPpMd), play a
critical role in the project's development.
## Fleets
@@ -87,7 +87,7 @@ This turns your on-prem cluster into a `dstack` fleet, ready to run dev environm
### GPU blocks
At `dstack`, when running a job on an instance, it uses all available GPUs on that instance. In Q1 2025, we will
-introduce [GPU blocks :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://github.com/dstackai/dstack/issues/1780){:target="_blank"},
+introduce [GPU blocks](https://github.com/dstackai/dstack/issues/1780),
allowing the allocation of instance GPUs into discrete blocks that can be reused by concurrent jobs.
This will enable more cost-efficient utilization of expensive instances.
@@ -112,16 +112,16 @@ for model deployment, and we continue to enhance support for the rest of NVIDIA'
This year, we’re particularly proud of our newly added integration with AMD.
`dstack` works seamlessly with any on-prem AMD clusters. For example, you can rent such servers through our partner
-[Hot Aisle :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://hotaisle.xyz/){:target="_blank"}.
+[Hot Aisle](https://hotaisle.xyz/).
-> Among cloud providers, [AMD :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://www.amd.com/en/products/accelerators/instinct.html){:target="_blank"} is supported only through RunPod. In Q1 2025, we plan to extend it to
-[Nscale :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://www.nscale.com/){:target="_blank"},
-> [Hot Aisle :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://hotaisle.xyz/){:target="_blank"}, and potentially other providers open to collaboration.
+> Among cloud providers, [AMD](https://www.amd.com/en/products/accelerators/instinct.html) is supported only through RunPod. In Q1 2025, we plan to extend it to
+[Nscale](https://www.nscale.com/),
+> [Hot Aisle](https://hotaisle.xyz/), and potentially other providers open to collaboration.
### Intel
In Q1 2025, our roadmap includes added integration with
-[Intel Gaudi :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://www.intel.com/content/www/us/en/products/details/processors/ai-accelerators/gaudi-overview.html){:target="_blank"}
+[Intel Gaudi](https://www.intel.com/content/www/us/en/products/details/processors/ai-accelerators/gaudi-overview.html)
among other accelerator chips.
## Join the community
diff --git a/docs/blog/posts/changelog-07-25.md b/docs/blog/posts/changelog-07-25.md
index 13bf67f54..909fa2859 100644
--- a/docs/blog/posts/changelog-07-25.md
+++ b/docs/blog/posts/changelog-07-25.md
@@ -112,7 +112,7 @@ resources:
#### Tenstorrent
-`dstack` remains committed to supporting multiple GPU vendors—including NVIDIA, AMD, TPUs, and more recently, [Tenstorrent :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://tenstorrent.com/){:target="_blank"}. The latest release improves Tenstorrent support by handling hosts with multiple N300 cards and adds Docker-in-Docker support.
+`dstack` remains committed to supporting multiple GPU vendors—including NVIDIA, AMD, TPUs, and more recently, [Tenstorrent](https://tenstorrent.com/). The latest release improves Tenstorrent support by handling hosts with multiple N300 cards and adds Docker-in-Docker support.
@@ -100,7 +100,7 @@ GPU partitioning is only practical if used dynamically—for instance, to run mu
#### Limitations
1. **Reproducibility**: AMD’s original blog post on partitioning lacked detailed setup information, so we had to reconstruct the benchmarks independently.
-2. **Network tuning**: These benchmarks were run on a default, out-of-the-box network configuration. Our results for RCCL (~339 GB/s) and RDMA (~726 Gbps) are slightly below the peak figures [reported by Dell :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://infohub.delltechnologies.com/en-us/l/generative-ai-in-the-enterprise-with-amd-accelerators/rccl-and-perftest-for-cluster-validation-1/4/){:target="_blank"}. This suggests that further performance could be unlocked with expert tuning of network topology, MTU size, and NCCL environment variables.
+2. **Network tuning**: These benchmarks were run on a default, out-of-the-box network configuration. Our results for RCCL (~339 GB/s) and RDMA (~726 Gbps) are slightly below the peak figures [reported by Dell](https://infohub.delltechnologies.com/en-us/l/generative-ai-in-the-enterprise-with-amd-accelerators/rccl-and-perftest-for-cluster-validation-1/4/). This suggests that further performance could be unlocked with expert tuning of network topology, MTU size, and NCCL environment variables.
## Benchmark setup
@@ -352,7 +352,7 @@ The `SIZE` value is `1M`, `2M`, .., `8G`.
**vLLM data parallel**
-1. Build nginx container (see [vLLM-nginx :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://docs.vllm.ai/en/stable/deployment/nginx.html#build-nginx-container){:target="_blank"}).
+1. Build nginx container (see [vLLM-nginx](https://docs.vllm.ai/en/stable/deployment/nginx.html#build-nginx-container)).
2. Create `nginx.conf`
@@ -471,13 +471,13 @@ HIP_VISIBLE_DEVICES=0 python3 toy_inference_benchmark.py \
## Source code
-All source code and findings are available in [our GitHub repo :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://github.com/dstackai/benchmarks/tree/main/amd/baremetal_container_partition){:target="_blank"}.
+All source code and findings are available in [our GitHub repo](https://github.com/dstackai/benchmarks/tree/main/amd/baremetal_container_partition).
## References
-* [AMD Instinct MI300X GPU partitioning overview :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://instinct.docs.amd.com/projects/amdgpu-docs/en/latest/gpu-partitioning/mi300x/overview.html){:target="_blank"}
-* [Deep dive into partition modes by AMD :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://rocm.blogs.amd.com/software-tools-optimization/compute-memory-modes/README.html){:target="_blank"}.
-* [RCCL and PerfTest for cluster validation by Dell :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://infohub.delltechnologies.com/en-us/l/generative-ai-in-the-enterprise-with-amd-accelerators/rccl-and-perftest-for-cluster-validation-1/4/){:target="_blank"}.
+* [AMD Instinct MI300X GPU partitioning overview](https://instinct.docs.amd.com/projects/amdgpu-docs/en/latest/gpu-partitioning/mi300x/overview.html)
+* [Deep dive into partition modes by AMD](https://rocm.blogs.amd.com/software-tools-optimization/compute-memory-modes/README.html).
+* [RCCL and PerfTest for cluster validation by Dell](https://infohub.delltechnologies.com/en-us/l/generative-ai-in-the-enterprise-with-amd-accelerators/rccl-and-perftest-for-cluster-validation-1/4/).
## What's next?
@@ -487,5 +487,5 @@ Benchmark the performance impact of VMs vs bare-metal for inference and training
#### Hot Aisle
-Big thanks to [Hot Aisle :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://hotaisle.xyz/){:target="_blank"} for providing the compute power behind these benchmarks.
+Big thanks to [Hot Aisle](https://hotaisle.xyz/) for providing the compute power behind these benchmarks.
If you’re looking for fast AMD GPU bare-metal or VM instances, they’re definitely worth checking out.
diff --git a/docs/blog/posts/benchmark-amd-vms.md b/docs/blog/posts/benchmark-amd-vms.md
index 099fee9be..b8d9105d0 100644
--- a/docs/blog/posts/benchmark-amd-vms.md
+++ b/docs/blog/posts/benchmark-amd-vms.md
@@ -18,7 +18,7 @@ This is the first in our series of benchmarks exploring the performance of AMD G
Our findings reveal that for single-GPU LLM training and inference, both setups deliver comparable performance. The subtle differences we observed highlight how virtualization overhead can influence performance under specific conditions, but for most practical purposes, the performance is nearly identical.
-This benchmark was supported by [Hot Aisle :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://hotaisle.xyz/){:target="_blank"},
+This benchmark was supported by [Hot Aisle](https://hotaisle.xyz/),
a provider of AMD GPU bare-metal and VM infrastructure.
## Benchmark 1: Inference
@@ -201,11 +201,11 @@ python3 trl/scripts/sft.py \
## Source code
-All source code and findings are available in our [GitHub repo :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://github.com/dstackai/benchmarks/tree/main/amd/single_gpu_vm_vs_bare-metal){:target="_blank"}.
+All source code and findings are available in our [GitHub repo](https://github.com/dstackai/benchmarks/tree/main/amd/single_gpu_vm_vs_bare-metal).
## References
-* [vLLM V1 Meets AMD Instinct GPUs: A New Era for LLM Inference Performance :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://rocm.blogs.amd.com/software-tools-optimization/vllmv1-rocm-llm/README.html){:target="_blank"}
+* [vLLM V1 Meets AMD Instinct GPUs: A New Era for LLM Inference Performance](https://rocm.blogs.amd.com/software-tools-optimization/vllmv1-rocm-llm/README.html)
## What's next?
@@ -215,5 +215,5 @@ Our next steps are to benchmark VM vs. bare-metal performance in multi-GPU and m
#### Hot Aisle
-Big thanks to [Hot Aisle :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://hotaisle.xyz/){:target="_blank"} for providing the compute power behind these benchmarks.
+Big thanks to [Hot Aisle](https://hotaisle.xyz/) for providing the compute power behind these benchmarks.
If you’re looking for fast AMD GPU bare-metal or VM instances, they’re definitely worth checking out.
diff --git a/docs/blog/posts/benchmarking-pd-ratios.md b/docs/blog/posts/benchmarking-pd-ratios.md
index 1069c5794..c303163e1 100644
--- a/docs/blog/posts/benchmarking-pd-ratios.md
+++ b/docs/blog/posts/benchmarking-pd-ratios.md
@@ -21,19 +21,19 @@ We evaluate different ratios across workload profiles and concurrency levels to
### What is Prefill–Decode disaggregation?
-LLM inference has two distinct phases: prefill and decode. Prefill processes all prompt tokens in parallel and is compute-intensive. Decode generates tokens one by one, repeatedly accessing the KV-cache, making it memory- and bandwidth-intensive. DistServe ([Zhong et al., 2024 :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://arxiv.org/pdf/2401.09670){:target="_blank"}) introduced prefill–decode disaggregation to separate these phases across dedicated workers, reducing interference and enabling hardware to be allocated more efficiently.
+LLM inference has two distinct phases: prefill and decode. Prefill processes all prompt tokens in parallel and is compute-intensive. Decode generates tokens one by one, repeatedly accessing the KV-cache, making it memory- and bandwidth-intensive. DistServe ([Zhong et al., 2024](https://arxiv.org/pdf/2401.09670)) introduced prefill–decode disaggregation to separate these phases across dedicated workers, reducing interference and enabling hardware to be allocated more efficiently.
### What is the prefill–decode ratio?
The ratio of prefill to decode workers determines how much capacity is dedicated to each phase. DistServe showed that for a workload with ISL=512 and OSL=64, a 2:1 ratio met both TTFT and TPOT targets. But this example does not answer how the ratio should be chosen more generally, or whether it needs to change at runtime.
!!! info "Reasoning model example"
- In the DeepSeek deployment ([LMSYS, 2025 :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://lmsys.org/blog/2025-05-05-large-scale-ep){:target="_blank"}), the ratio was 1:3. This decode-leaning split reflects reasoning workloads, where long outputs dominate. Allocating more workers to decode reduces inter-token latency and keeps responses streaming smoothly.
+ In the DeepSeek deployment ([LMSYS, 2025](https://lmsys.org/blog/2025-05-05-large-scale-ep)), the ratio was 1:3. This decode-leaning split reflects reasoning workloads, where long outputs dominate. Allocating more workers to decode reduces inter-token latency and keeps responses streaming smoothly.
### Dynamic ratio
-Dynamic approaches, such as NVIDIA’s [SLA-based :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://docs.nvidia.com/dynamo/latest/architecture/sla_planner.html){:target="_blank"}
-and [Load-based :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://docs.nvidia.com/dynamo/latest/architecture/load_planner.html){:target="_blank"} planners, adjust the ratio at runtime according to SLO targets or load. However, they do this in conjunction with auto-scaling, which increases orchestration complexity. This raises the question: does the prefill–decode ratio really need to be dynamic, or can a fixed ratio be chosen ahead of time and still provide robust performance?
+Dynamic approaches, such as NVIDIA’s [SLA-based](https://docs.nvidia.com/dynamo/latest/architecture/sla_planner.html)
+and [Load-based](https://docs.nvidia.com/dynamo/latest/architecture/load_planner.html) planners, adjust the ratio at runtime according to SLO targets or load. However, they do this in conjunction with auto-scaling, which increases orchestration complexity. This raises the question: does the prefill–decode ratio really need to be dynamic, or can a fixed ratio be chosen ahead of time and still provide robust performance?
## Benchmark purpose
@@ -72,7 +72,7 @@ If a fixed ratio consistently performs well across these metrics, it would indic
* **Model**: `openai/gpt-oss-120b`
* **Backend**: SGLang
-For full steps and raw data, see the [GitHub repo :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://github.com/dstackai/benchmarks/tree/main/comparison/pd_ratio){:target="_blank"}.
+For full steps and raw data, see the [GitHub repo](https://github.com/dstackai/benchmarks/tree/main/comparison/pd_ratio).
## Finding 1: Prefill-heavy workloads
@@ -134,8 +134,8 @@ Overall, more study on how the optimal ratio is found and what factors it depend
## References
-* [DistServe :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://arxiv.org/pdf/2401.09670){:target="_blank"}
-* [DeepSeek deployment on 96 H100 GPUs :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://lmsys.org/blog/2025-05-05-large-scale-ep/){:target="_blank"}
-* [Dynamo disaggregated serving :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://docs.nvidia.com/dynamo/latest/architecture/disagg_serving.html#){:target="_blank"}
-* [SGLang PD disaggregation :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://docs.sglang.ai/advanced_features/pd_disaggregation.html){:target="_blank"}
-* [vLLM disaggregated prefilling :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://docs.vllm.ai/en/v0.9.2/features/disagg_prefill.html){:target="_blank"}
+* [DistServe](https://arxiv.org/pdf/2401.09670)
+* [DeepSeek deployment on 96 H100 GPUs](https://lmsys.org/blog/2025-05-05-large-scale-ep/)
+* [Dynamo disaggregated serving](https://docs.nvidia.com/dynamo/latest/architecture/disagg_serving.html#)
+* [SGLang PD disaggregation](https://docs.sglang.ai/advanced_features/pd_disaggregation.html)
+* [vLLM disaggregated prefilling](https://docs.vllm.ai/en/v0.9.2/features/disagg_prefill.html)
diff --git a/docs/blog/posts/beyond-kubernetes-2024-recap-and-whats-ahead.md b/docs/blog/posts/beyond-kubernetes-2024-recap-and-whats-ahead.md
index dec4945ed..4c6b43f9b 100644
--- a/docs/blog/posts/beyond-kubernetes-2024-recap-and-whats-ahead.md
+++ b/docs/blog/posts/beyond-kubernetes-2024-recap-and-whats-ahead.md
@@ -21,25 +21,25 @@ As 2024 comes to a close, we reflect on the milestones we've achieved and look a
While `dstack` integrates with leading cloud GPU providers, we aim to expand partnerships with more providers
sharing our vision of simplifying AI infrastructure orchestration with a lightweight, efficient alternative to Kubernetes.
-This year, we’re excited to welcome our first partners: [Lambda :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://lambdalabs.com/){:target="_blank"},
-[RunPod :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://www.runpod.io/){:target="_blank"},
-[CUDO Compute :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://www.cudocompute.com/){:target="_blank"},
-and [Hot Aisle :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://hotaisle.xyz/){:target="_blank"}.
+This year, we’re excited to welcome our first partners: [Lambda](https://lambdalabs.com/),
+[RunPod](https://www.runpod.io/),
+[CUDO Compute](https://www.cudocompute.com/),
+and [Hot Aisle](https://hotaisle.xyz/).
-We’d also like to thank [Oracle :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://www.oracle.com/cloud/){:target="_blank"}
+We’d also like to thank [Oracle ](https://www.oracle.com/cloud/)
for their collaboration, ensuring seamless integration between `dstack` and OCI.
-> Special thanks to [Lambda :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://lambdalabs.com/){:target="_blank"} and
-> [Hot Aisle :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://hotaisle.xyz/){:target="_blank"} for providing NVIDIA and AMD hardware, enabling us conducting
+> Special thanks to [Lambda](https://lambdalabs.com/) and
+> [Hot Aisle](https://hotaisle.xyz/) for providing NVIDIA and AMD hardware, enabling us conducting
> [benchmarks](/blog/category/benchmarks/), which
> are essential to advancing open-source inference and training stacks for all accelerator chips.
## Community
Thanks to your support, the project has
-reached [1.6K stars on GitHub :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://github.com/dstackai/dstack){:target="_blank"},
+reached [1.6K stars on GitHub](https://github.com/dstackai/dstack),
reflecting the growing interest and trust in its mission.
-Your issues, pull requests, as well as feedback on [Discord :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://discord.gg/u8SmfwPpMd){:target="_blank"}, play a
+Your issues, pull requests, as well as feedback on [Discord](https://discord.gg/u8SmfwPpMd), play a
critical role in the project's development.
## Fleets
@@ -87,7 +87,7 @@ This turns your on-prem cluster into a `dstack` fleet, ready to run dev environm
### GPU blocks
At `dstack`, when running a job on an instance, it uses all available GPUs on that instance. In Q1 2025, we will
-introduce [GPU blocks :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://github.com/dstackai/dstack/issues/1780){:target="_blank"},
+introduce [GPU blocks](https://github.com/dstackai/dstack/issues/1780),
allowing the allocation of instance GPUs into discrete blocks that can be reused by concurrent jobs.
This will enable more cost-efficient utilization of expensive instances.
@@ -112,16 +112,16 @@ for model deployment, and we continue to enhance support for the rest of NVIDIA'
This year, we’re particularly proud of our newly added integration with AMD.
`dstack` works seamlessly with any on-prem AMD clusters. For example, you can rent such servers through our partner
-[Hot Aisle :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://hotaisle.xyz/){:target="_blank"}.
+[Hot Aisle](https://hotaisle.xyz/).
-> Among cloud providers, [AMD :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://www.amd.com/en/products/accelerators/instinct.html){:target="_blank"} is supported only through RunPod. In Q1 2025, we plan to extend it to
-[Nscale :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://www.nscale.com/){:target="_blank"},
-> [Hot Aisle :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://hotaisle.xyz/){:target="_blank"}, and potentially other providers open to collaboration.
+> Among cloud providers, [AMD](https://www.amd.com/en/products/accelerators/instinct.html) is supported only through RunPod. In Q1 2025, we plan to extend it to
+[Nscale](https://www.nscale.com/),
+> [Hot Aisle](https://hotaisle.xyz/), and potentially other providers open to collaboration.
### Intel
In Q1 2025, our roadmap includes added integration with
-[Intel Gaudi :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://www.intel.com/content/www/us/en/products/details/processors/ai-accelerators/gaudi-overview.html){:target="_blank"}
+[Intel Gaudi](https://www.intel.com/content/www/us/en/products/details/processors/ai-accelerators/gaudi-overview.html)
among other accelerator chips.
## Join the community
diff --git a/docs/blog/posts/changelog-07-25.md b/docs/blog/posts/changelog-07-25.md
index 13bf67f54..909fa2859 100644
--- a/docs/blog/posts/changelog-07-25.md
+++ b/docs/blog/posts/changelog-07-25.md
@@ -112,7 +112,7 @@ resources:
#### Tenstorrent
-`dstack` remains committed to supporting multiple GPU vendors—including NVIDIA, AMD, TPUs, and more recently, [Tenstorrent :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://tenstorrent.com/){:target="_blank"}. The latest release improves Tenstorrent support by handling hosts with multiple N300 cards and adds Docker-in-Docker support.
+`dstack` remains committed to supporting multiple GPU vendors—including NVIDIA, AMD, TPUs, and more recently, [Tenstorrent](https://tenstorrent.com/). The latest release improves Tenstorrent support by handling hosts with multiple N300 cards and adds Docker-in-Docker support.
 @@ -192,7 +192,7 @@ Server-side performance has been improved. With optimized handling and backgroun
#### Google SSO
-Alongside the open-source version, `dstack` also offers [dstack Enterprise :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://github.com/dstackai/dstack-enterprise){:target="_blank"} — which adds dedicated support and extra integrations like Single Sign-On (SSO). The latest release introduces support for configuring your company’s Google account for authentication.
+Alongside the open-source version, `dstack` also offers [dstack Enterprise](https://github.com/dstackai/dstack-enterprise) — which adds dedicated support and extra integrations like Single Sign-On (SSO). The latest release introduces support for configuring your company’s Google account for authentication.
@@ -192,7 +192,7 @@ Server-side performance has been improved. With optimized handling and backgroun
#### Google SSO
-Alongside the open-source version, `dstack` also offers [dstack Enterprise :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://github.com/dstackai/dstack-enterprise){:target="_blank"} — which adds dedicated support and extra integrations like Single Sign-On (SSO). The latest release introduces support for configuring your company’s Google account for authentication.
+Alongside the open-source version, `dstack` also offers [dstack Enterprise](https://github.com/dstackai/dstack-enterprise) — which adds dedicated support and extra integrations like Single Sign-On (SSO). The latest release introduces support for configuring your company’s Google account for authentication.
 @@ -201,4 +201,4 @@ If you’d like to learn more about `dstack` Enterprise, [let us know](https://c
That’s all for now.
!!! info "What's next?"
- Give dstack a try, and share your feedback—whether it’s [GitHub :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://github.com/dstackai/dstack){:target="_blank"} issues, PRs, or questions on [Discord :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://discord.gg/u8SmfwPpMd){:target="_blank"}. We’re eager to hear from you!
+ Give dstack a try, and share your feedback—whether it’s [GitHub](https://github.com/dstackai/dstack) issues, PRs, or questions on [Discord](https://discord.gg/u8SmfwPpMd). We’re eager to hear from you!
diff --git a/docs/blog/posts/cursor.md b/docs/blog/posts/cursor.md
index a5f960469..4e8e01fb4 100644
--- a/docs/blog/posts/cursor.md
+++ b/docs/blog/posts/cursor.md
@@ -15,7 +15,7 @@ automatic repository fetching, and streamlined access via SSH or a preferred des
Previously, support was limited to VS Code. However, as developers rely on a variety of desktop IDEs,
we’ve expanded compatibility. With this update, dev environments now offer effortless access for users of
-[Cursor :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://www.cursor.com/){:target="_blank"}.
+[Cursor](https://www.cursor.com/).
@@ -201,4 +201,4 @@ If you’d like to learn more about `dstack` Enterprise, [let us know](https://c
That’s all for now.
!!! info "What's next?"
- Give dstack a try, and share your feedback—whether it’s [GitHub :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://github.com/dstackai/dstack){:target="_blank"} issues, PRs, or questions on [Discord :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://discord.gg/u8SmfwPpMd){:target="_blank"}. We’re eager to hear from you!
+ Give dstack a try, and share your feedback—whether it’s [GitHub](https://github.com/dstackai/dstack) issues, PRs, or questions on [Discord](https://discord.gg/u8SmfwPpMd). We’re eager to hear from you!
diff --git a/docs/blog/posts/cursor.md b/docs/blog/posts/cursor.md
index a5f960469..4e8e01fb4 100644
--- a/docs/blog/posts/cursor.md
+++ b/docs/blog/posts/cursor.md
@@ -15,7 +15,7 @@ automatic repository fetching, and streamlined access via SSH or a preferred des
Previously, support was limited to VS Code. However, as developers rely on a variety of desktop IDEs,
we’ve expanded compatibility. With this update, dev environments now offer effortless access for users of
-[Cursor :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://www.cursor.com/){:target="_blank"}.
+[Cursor](https://www.cursor.com/).
 @@ -79,8 +79,8 @@ Using Cursor over VS Code offers multiple benefits, particularly when it comes t
enhanced developer experience.
!!! info "What's next?"
- 1. [Download :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://www.cursor.com/){:target="_blank"} and install Cursor
+ 1. [Download](https://www.cursor.com/) and install Cursor
2. Learn more about [dev environments](../../docs/concepts/dev-environments.md),
[tasks](../../docs/concepts/tasks.md), [services](../../docs/concepts/services.md),
and [fleets](../../docs/concepts/fleets.md)
- 2. Join [Discord :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://discord.gg/u8SmfwPpMd){:target="_blank"}
+ 2. Join [Discord](https://discord.gg/u8SmfwPpMd)
diff --git a/docs/blog/posts/digitalocean-and-amd-dev-cloud.md b/docs/blog/posts/digitalocean-and-amd-dev-cloud.md
index 4103e6e15..ce400899d 100644
--- a/docs/blog/posts/digitalocean-and-amd-dev-cloud.md
+++ b/docs/blog/posts/digitalocean-and-amd-dev-cloud.md
@@ -12,8 +12,8 @@ categories:
Orchestration automates provisioning, running jobs, and tearing them down. While Kubernetes and Slurm are powerful in their domains, they lack the lightweight, GPU-native focus modern teams need to move faster.
-`dstack` is built entirely around GPUs. Our latest update introduces native integration with [DigitalOcean :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://www.digitalocean.com/products/gradient/gpu-droplets){:target="_blank"} and
-[AMD Developer Cloud :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://www.amd.com/en/developer/resources/cloud-access/amd-developer-cloud.html){:target="_blank"}, enabling teams to provision cloud GPUs and run workloads more cost-efficiently.
+`dstack` is built entirely around GPUs. Our latest update introduces native integration with [DigitalOcean](https://www.digitalocean.com/products/gradient/gpu-droplets) and
+[AMD Developer Cloud](https://www.amd.com/en/developer/resources/cloud-access/amd-developer-cloud.html), enabling teams to provision cloud GPUs and run workloads more cost-efficiently.
@@ -79,8 +79,8 @@ Using Cursor over VS Code offers multiple benefits, particularly when it comes t
enhanced developer experience.
!!! info "What's next?"
- 1. [Download :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://www.cursor.com/){:target="_blank"} and install Cursor
+ 1. [Download](https://www.cursor.com/) and install Cursor
2. Learn more about [dev environments](../../docs/concepts/dev-environments.md),
[tasks](../../docs/concepts/tasks.md), [services](../../docs/concepts/services.md),
and [fleets](../../docs/concepts/fleets.md)
- 2. Join [Discord :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://discord.gg/u8SmfwPpMd){:target="_blank"}
+ 2. Join [Discord](https://discord.gg/u8SmfwPpMd)
diff --git a/docs/blog/posts/digitalocean-and-amd-dev-cloud.md b/docs/blog/posts/digitalocean-and-amd-dev-cloud.md
index 4103e6e15..ce400899d 100644
--- a/docs/blog/posts/digitalocean-and-amd-dev-cloud.md
+++ b/docs/blog/posts/digitalocean-and-amd-dev-cloud.md
@@ -12,8 +12,8 @@ categories:
Orchestration automates provisioning, running jobs, and tearing them down. While Kubernetes and Slurm are powerful in their domains, they lack the lightweight, GPU-native focus modern teams need to move faster.
-`dstack` is built entirely around GPUs. Our latest update introduces native integration with [DigitalOcean :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://www.digitalocean.com/products/gradient/gpu-droplets){:target="_blank"} and
-[AMD Developer Cloud :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://www.amd.com/en/developer/resources/cloud-access/amd-developer-cloud.html){:target="_blank"}, enabling teams to provision cloud GPUs and run workloads more cost-efficiently.
+`dstack` is built entirely around GPUs. Our latest update introduces native integration with [DigitalOcean](https://www.digitalocean.com/products/gradient/gpu-droplets) and
+[AMD Developer Cloud](https://www.amd.com/en/developer/resources/cloud-access/amd-developer-cloud.html), enabling teams to provision cloud GPUs and run workloads more cost-efficiently.
 @@ -143,9 +143,9 @@ $ dstack apply -f examples/models/gpt-oss/120b.dstack.yml
!!! info "What's next?"
1. Check [Quickstart](../../docs/quickstart.md)
- 2. Learn more about [DigitalOcean :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://www.digitalocean.com/products/gradient/gpu-droplets){:target="_blank"} and
- [AMD Developer Cloud :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://www.amd.com/en/developer/resources/cloud-access/amd-developer-cloud.html){:target="_blank"}
+ 2. Learn more about [DigitalOcean](https://www.digitalocean.com/products/gradient/gpu-droplets) and
+ [AMD Developer Cloud](https://www.amd.com/en/developer/resources/cloud-access/amd-developer-cloud.html)
3. Explore [dev environments](../../docs/concepts/dev-environments.md),
[tasks](../../docs/concepts/tasks.md), [services](../../docs/concepts/services.md),
and [fleets](../../docs/concepts/fleets.md)
- 4. Join [Discord :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://discord.gg/u8SmfwPpMd){:target="_blank"}
+ 4. Join [Discord](https://discord.gg/u8SmfwPpMd)
diff --git a/docs/blog/posts/docker-inside-containers.md b/docs/blog/posts/docker-inside-containers.md
index 13af39030..699e75fe7 100644
--- a/docs/blog/posts/docker-inside-containers.md
+++ b/docs/blog/posts/docker-inside-containers.md
@@ -94,12 +94,12 @@ Last but not least, you can, of course, use the `docker run` command, for exampl
## Examples
-A few examples of using this feature can be found in [`examples/misc/docker-compose` :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://github.com/dstackai/dstack/blob/master/examples/misc/docker-compose){: target="_ blank"}.
+A few examples of using this feature can be found in [`examples/misc/docker-compose`](https://github.com/dstackai/dstack/blob/master/examples/misc/docker-compose).
## Feedback
If you find something not working as intended, please be sure to report it to
-our [bug tracker :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://github.com/dstackai/dstack/issues){:target="_ blank"}.
+our [bug tracker](https://github.com/dstackai/dstack/issues){:target="_ blank"}.
Your feedback and feature requests are also very welcome on both
-[Discord :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://discord.gg/u8SmfwPpMd){:target="_blank"} and the
-[issue tracker :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://github.com/dstackai/dstack/issues){:target="_blank"}.
+[Discord](https://discord.gg/u8SmfwPpMd) and the
+[issue tracker](https://github.com/dstackai/dstack/issues).
diff --git a/docs/blog/posts/dstack-metrics.md b/docs/blog/posts/dstack-metrics.md
index f4647d782..4558cd0cc 100644
--- a/docs/blog/posts/dstack-metrics.md
+++ b/docs/blog/posts/dstack-metrics.md
@@ -63,7 +63,7 @@ Monitoring is a critical part of observability, and we have many more features o
## Feedback
If you find something not working as intended, please be sure to report it to
-our [bug tracker :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://github.com/dstackai/dstack/issues){:target="_ blank"}.
+our [bug tracker](https://github.com/dstackai/dstack/issues){:target="_ blank"}.
Your feedback and feature requests are also very welcome on both
-[Discord :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://discord.gg/u8SmfwPpMd){:target="_blank"} and the
-[issue tracker :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://github.com/dstackai/dstack/issues){:target="_blank"}.
+[Discord](https://discord.gg/u8SmfwPpMd) and the
+[issue tracker](https://github.com/dstackai/dstack/issues).
diff --git a/docs/blog/posts/dstack-sky-own-cloud-accounts.md b/docs/blog/posts/dstack-sky-own-cloud-accounts.md
index 16b68867c..13c927a31 100644
--- a/docs/blog/posts/dstack-sky-own-cloud-accounts.md
+++ b/docs/blog/posts/dstack-sky-own-cloud-accounts.md
@@ -9,7 +9,7 @@ categories:
# dstack Sky now supports your own cloud accounts
-[dstack Sky :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://sky.dstack.ai){:target="_blank"}
+[dstack Sky](https://sky.dstack.ai)
enables you to access GPUs from the global marketplace at the most
competitive rates. However, sometimes you may want to use your own cloud accounts.
With today's release, both options are now supported.
@@ -30,12 +30,12 @@ CUDO, RunPod, and Vast.ai.
Additionally, you can disable certain backends if you do not plan to use them.
Typically, if you prefer using your own cloud accounts, it's recommended that you use the
-[open-source version :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://github.com/dstackai/dstack/){:target="_blank"} of `dstack`.
+[open-source version](https://github.com/dstackai/dstack/) of `dstack`.
However, if you prefer not to host it yourself, now you can use `dstack Sky`
with your own cloud accounts as well.
> Seeking the cheapest on-demand and spot cloud GPUs?
-> [dstack Sky :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://sky.dstack.ai){:target="_blank"} has you covered!
+> [dstack Sky](https://sky.dstack.ai) has you covered!
Need help, have a question, or just want to stay updated?
diff --git a/docs/blog/posts/ea-gtc25.md b/docs/blog/posts/ea-gtc25.md
index 262554866..b7a28ba59 100644
--- a/docs/blog/posts/ea-gtc25.md
+++ b/docs/blog/posts/ea-gtc25.md
@@ -12,7 +12,7 @@ links:
# How EA uses dstack to fast-track AI development
-At NVIDIA GTC 2025, Electronic Arts [shared :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://www.nvidia.com/en-us/on-demand/session/gtc25-s73667/){:target="_blank"} how they’re scaling AI development and managing infrastructure across teams. They highlighted using tools like `dstack` to provision GPUs quickly, flexibly, and cost-efficiently. This case study summarizes key insights from their talk.
+At NVIDIA GTC 2025, Electronic Arts [shared](https://www.nvidia.com/en-us/on-demand/session/gtc25-s73667/) how they’re scaling AI development and managing infrastructure across teams. They highlighted using tools like `dstack` to provision GPUs quickly, flexibly, and cost-efficiently. This case study summarizes key insights from their talk.
@@ -143,9 +143,9 @@ $ dstack apply -f examples/models/gpt-oss/120b.dstack.yml
!!! info "What's next?"
1. Check [Quickstart](../../docs/quickstart.md)
- 2. Learn more about [DigitalOcean :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://www.digitalocean.com/products/gradient/gpu-droplets){:target="_blank"} and
- [AMD Developer Cloud :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://www.amd.com/en/developer/resources/cloud-access/amd-developer-cloud.html){:target="_blank"}
+ 2. Learn more about [DigitalOcean](https://www.digitalocean.com/products/gradient/gpu-droplets) and
+ [AMD Developer Cloud](https://www.amd.com/en/developer/resources/cloud-access/amd-developer-cloud.html)
3. Explore [dev environments](../../docs/concepts/dev-environments.md),
[tasks](../../docs/concepts/tasks.md), [services](../../docs/concepts/services.md),
and [fleets](../../docs/concepts/fleets.md)
- 4. Join [Discord :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://discord.gg/u8SmfwPpMd){:target="_blank"}
+ 4. Join [Discord](https://discord.gg/u8SmfwPpMd)
diff --git a/docs/blog/posts/docker-inside-containers.md b/docs/blog/posts/docker-inside-containers.md
index 13af39030..699e75fe7 100644
--- a/docs/blog/posts/docker-inside-containers.md
+++ b/docs/blog/posts/docker-inside-containers.md
@@ -94,12 +94,12 @@ Last but not least, you can, of course, use the `docker run` command, for exampl
## Examples
-A few examples of using this feature can be found in [`examples/misc/docker-compose` :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://github.com/dstackai/dstack/blob/master/examples/misc/docker-compose){: target="_ blank"}.
+A few examples of using this feature can be found in [`examples/misc/docker-compose`](https://github.com/dstackai/dstack/blob/master/examples/misc/docker-compose).
## Feedback
If you find something not working as intended, please be sure to report it to
-our [bug tracker :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://github.com/dstackai/dstack/issues){:target="_ blank"}.
+our [bug tracker](https://github.com/dstackai/dstack/issues){:target="_ blank"}.
Your feedback and feature requests are also very welcome on both
-[Discord :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://discord.gg/u8SmfwPpMd){:target="_blank"} and the
-[issue tracker :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://github.com/dstackai/dstack/issues){:target="_blank"}.
+[Discord](https://discord.gg/u8SmfwPpMd) and the
+[issue tracker](https://github.com/dstackai/dstack/issues).
diff --git a/docs/blog/posts/dstack-metrics.md b/docs/blog/posts/dstack-metrics.md
index f4647d782..4558cd0cc 100644
--- a/docs/blog/posts/dstack-metrics.md
+++ b/docs/blog/posts/dstack-metrics.md
@@ -63,7 +63,7 @@ Monitoring is a critical part of observability, and we have many more features o
## Feedback
If you find something not working as intended, please be sure to report it to
-our [bug tracker :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://github.com/dstackai/dstack/issues){:target="_ blank"}.
+our [bug tracker](https://github.com/dstackai/dstack/issues){:target="_ blank"}.
Your feedback and feature requests are also very welcome on both
-[Discord :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://discord.gg/u8SmfwPpMd){:target="_blank"} and the
-[issue tracker :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://github.com/dstackai/dstack/issues){:target="_blank"}.
+[Discord](https://discord.gg/u8SmfwPpMd) and the
+[issue tracker](https://github.com/dstackai/dstack/issues).
diff --git a/docs/blog/posts/dstack-sky-own-cloud-accounts.md b/docs/blog/posts/dstack-sky-own-cloud-accounts.md
index 16b68867c..13c927a31 100644
--- a/docs/blog/posts/dstack-sky-own-cloud-accounts.md
+++ b/docs/blog/posts/dstack-sky-own-cloud-accounts.md
@@ -9,7 +9,7 @@ categories:
# dstack Sky now supports your own cloud accounts
-[dstack Sky :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://sky.dstack.ai){:target="_blank"}
+[dstack Sky](https://sky.dstack.ai)
enables you to access GPUs from the global marketplace at the most
competitive rates. However, sometimes you may want to use your own cloud accounts.
With today's release, both options are now supported.
@@ -30,12 +30,12 @@ CUDO, RunPod, and Vast.ai.
Additionally, you can disable certain backends if you do not plan to use them.
Typically, if you prefer using your own cloud accounts, it's recommended that you use the
-[open-source version :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://github.com/dstackai/dstack/){:target="_blank"} of `dstack`.
+[open-source version](https://github.com/dstackai/dstack/) of `dstack`.
However, if you prefer not to host it yourself, now you can use `dstack Sky`
with your own cloud accounts as well.
> Seeking the cheapest on-demand and spot cloud GPUs?
-> [dstack Sky :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://sky.dstack.ai){:target="_blank"} has you covered!
+> [dstack Sky](https://sky.dstack.ai) has you covered!
Need help, have a question, or just want to stay updated?
diff --git a/docs/blog/posts/ea-gtc25.md b/docs/blog/posts/ea-gtc25.md
index 262554866..b7a28ba59 100644
--- a/docs/blog/posts/ea-gtc25.md
+++ b/docs/blog/posts/ea-gtc25.md
@@ -12,7 +12,7 @@ links:
# How EA uses dstack to fast-track AI development
-At NVIDIA GTC 2025, Electronic Arts [shared :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://www.nvidia.com/en-us/on-demand/session/gtc25-s73667/){:target="_blank"} how they’re scaling AI development and managing infrastructure across teams. They highlighted using tools like `dstack` to provision GPUs quickly, flexibly, and cost-efficiently. This case study summarizes key insights from their talk.
+At NVIDIA GTC 2025, Electronic Arts [shared](https://www.nvidia.com/en-us/on-demand/session/gtc25-s73667/) how they’re scaling AI development and managing infrastructure across teams. They highlighted using tools like `dstack` to provision GPUs quickly, flexibly, and cost-efficiently. This case study summarizes key insights from their talk.
 @@ -80,7 +80,7 @@ Workflows became standardized, reproducible, and easier to trace—thanks to the
By adopting tools that are cloud-agnostic and developer-friendly, EA has reduced friction—from provisioning GPUs to deploying models—and enabled teams to spend more time on actual ML work.
-*Huge thanks to Kris and Keng from EA’s central tech team for sharing these insights. For more details, including the recording and slides, check out the full talk on the [NVIDIA GTC website :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://www.nvidia.com/en-us/on-demand/session/gtc25-s73667/){:target="_blank"}.*
+*Huge thanks to Kris and Keng from EA’s central tech team for sharing these insights. For more details, including the recording and slides, check out the full talk on the [NVIDIA GTC website](https://www.nvidia.com/en-us/on-demand/session/gtc25-s73667/).*
!!! info "What's next?"
1. Check [dev environments](../../docs/concepts/dev-environments.md), [tasks](../../docs/concepts/tasks.md), [services](../../docs/concepts/services.md), and [fleets](../../docs/concepts/fleets.md)
diff --git a/docs/blog/posts/gh200-on-lambda.md b/docs/blog/posts/gh200-on-lambda.md
index e7831a76c..1a87dc90e 100644
--- a/docs/blog/posts/gh200-on-lambda.md
+++ b/docs/blog/posts/gh200-on-lambda.md
@@ -42,7 +42,7 @@ The GH200 Superchip’s 450 GB/s bidirectional bandwidth enables KV cache offloa
## GH200 on Lambda
-[Lambda :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://cloud.lambda.ai/sign-up?_gl=1*1qovk06*_gcl_au*MTg2MDc3OTAyOS4xNzQyOTA3Nzc0LjE3NDkwNTYzNTYuMTc0NTQxOTE2MS4xNzQ1NDE5MTYw*_ga*MTE2NDM5MzI0My4xNzQyOTA3Nzc0*_ga_43EZT1FM6Q*czE3NDY3MTczOTYkbzM0JGcxJHQxNzQ2NzE4MDU2JGo1NyRsMCRoMTU0Mzg1NTU1OQ..){:target="_blank"} provides secure, user-friendly, reliable, and affordable cloud GPUs. Since end of last year, Lambda started to offer on-demand GH200 instances through their public cloud. Furthermore, they offer these instances at the promotional price of $1.49 per hour until June 30th 2025.
+[Lambda](https://cloud.lambda.ai/sign-up?_gl=1*1qovk06*_gcl_au*MTg2MDc3OTAyOS4xNzQyOTA3Nzc0LjE3NDkwNTYzNTYuMTc0NTQxOTE2MS4xNzQ1NDE5MTYw*_ga*MTE2NDM5MzI0My4xNzQyOTA3Nzc0*_ga_43EZT1FM6Q*czE3NDY3MTczOTYkbzM0JGcxJHQxNzQ2NzE4MDU2JGo1NyRsMCRoMTU0Mzg1NTU1OQ..) provides secure, user-friendly, reliable, and affordable cloud GPUs. Since end of last year, Lambda started to offer on-demand GH200 instances through their public cloud. Furthermore, they offer these instances at the promotional price of $1.49 per hour until June 30th 2025.
With the latest `dstack` update, it’s now possible to use these instances with your Lambda account whether you’re running a dev environment, task, or service:
@@ -81,7 +81,7 @@ $ dstack apply -f .dstack.yml
> If you have GH200 or GB200-powered hosts already provisioned via Lambda, another cloud provider, or on-prem, you can now use them with [SSH fleets](../../docs/concepts/fleets.md#ssh-fleets).
!!! info "What's next?"
- 1. Sign up with [Lambda :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://cloud.lambda.ai/sign-up?_gl=1*1qovk06*_gcl_au*MTg2MDc3OTAyOS4xNzQyOTA3Nzc0LjE3NDkwNTYzNTYuMTc0NTQxOTE2MS4xNzQ1NDE5MTYw*_ga*MTE2NDM5MzI0My4xNzQyOTA3Nzc0*_ga_43EZT1FM6Q*czE3NDY3MTczOTYkbzM0JGcxJHQxNzQ2NzE4MDU2JGo1NyRsMCRoMTU0Mzg1NTU1OQ..){:target="_blank"}
+ 1. Sign up with [Lambda](https://cloud.lambda.ai/sign-up?_gl=1*1qovk06*_gcl_au*MTg2MDc3OTAyOS4xNzQyOTA3Nzc0LjE3NDkwNTYzNTYuMTc0NTQxOTE2MS4xNzQ1NDE5MTYw*_ga*MTE2NDM5MzI0My4xNzQyOTA3Nzc0*_ga_43EZT1FM6Q*czE3NDY3MTczOTYkbzM0JGcxJHQxNzQ2NzE4MDU2JGo1NyRsMCRoMTU0Mzg1NTU1OQ..)
2. Set up the [Lambda](../../docs/concepts/backends.md#lambda) backend
3. Follow [Quickstart](../../docs/quickstart.md)
4. Check [dev environments](../../docs/concepts/dev-environments.md), [tasks](../../docs/concepts/tasks.md), [services](../../docs/concepts/services.md), and [fleets](../../docs/concepts/fleets.md)
diff --git a/docs/blog/posts/gpu-blocks-and-proxy-jump.md b/docs/blog/posts/gpu-blocks-and-proxy-jump.md
index cbf9ab7dc..61f28ea81 100644
--- a/docs/blog/posts/gpu-blocks-and-proxy-jump.md
+++ b/docs/blog/posts/gpu-blocks-and-proxy-jump.md
@@ -39,7 +39,7 @@ enables optimal hardware utilization by allowing concurrent workloads to run on
available resources on each host.
> For example, imagine you’ve reserved a cluster with multiple bare-metal nodes, each equipped with 8x MI300X GPUs from
-[Hot Aisle :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://hotaisle.xyz/){:target="_blank"}.
+[Hot Aisle](https://hotaisle.xyz/).
With `dstack`, you can define your fleet configuration like this:
@@ -108,7 +108,7 @@ The latest `dstack` release introduces the [`proxy_jump`](../../docs/concepts/fl
through a login node.
> For example, imagine you’ve reserved a 1-Click Cluster from
-> [Lambda :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://lambdalabs.com/){:target="_blank"} with multiple nodes, each equipped with 8x H100 GPUs from.
+> [Lambda](https://lambdalabs.com/) with multiple nodes, each equipped with 8x H100 GPUs from.
With `dstack`, you can define your fleet configuration like this:
@@ -174,8 +174,8 @@ an AI-native experience, simplicity, and vendor-agnostic orchestration for both
!!! info "Roadmap"
We plan to further enhance `dstack`'s support for both cloud and on-premises setups. For more details on our roadmap,
- refer to our [GitHub :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://github.com/dstackai/dstack/issues/2184){:target="_blank"}.
+ refer to our [GitHub](https://github.com/dstackai/dstack/issues/2184).
> Have questions? You're welcome to join
-> our [Discord :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://discord.gg/u8SmfwPpMd){:target="_blank"} or talk
-> directly to [our team :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://calendly.com/dstackai/discovery-call){:target="_blank"}.
+> our [Discord](https://discord.gg/u8SmfwPpMd) or talk
+> directly to [our team](https://calendly.com/dstackai/discovery-call).
diff --git a/docs/blog/posts/gpu-health-checks.md b/docs/blog/posts/gpu-health-checks.md
index 1571935b6..cc28bb96a 100644
--- a/docs/blog/posts/gpu-health-checks.md
+++ b/docs/blog/posts/gpu-health-checks.md
@@ -64,10 +64,10 @@ Passive GPU health checks work on AWS (except with custom `os_images`), Azure (e
This update is about visibility: giving engineers real-time insight into GPU health before jobs run. Next comes automation — policies to skip GPUs with warnings, and self-healing workflows that replace unhealthy instances without manual steps.
If you have experience with GPU reliability or ideas for automated recovery, join the conversation on
-[Discord :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://discord.gg/u8SmfwPpMd){:target="_blank"}.
+[Discord](https://discord.gg/u8SmfwPpMd).
!!! info "What's next?"
1. Check [Quickstart](../../docs/quickstart.md)
2. Explore the [clusters](../../docs/guides/clusters.md) guide
3. Learn more about [metrics](../../docs/guides/metrics.md)
- 4. Join [Discord :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://discord.gg/u8SmfwPpMd){:target="_blank"}
+ 4. Join [Discord](https://discord.gg/u8SmfwPpMd)
diff --git a/docs/blog/posts/h100-mi300x-inference-benchmark.md b/docs/blog/posts/h100-mi300x-inference-benchmark.md
index 350795684..2209393d1 100644
--- a/docs/blog/posts/h100-mi300x-inference-benchmark.md
+++ b/docs/blog/posts/h100-mi300x-inference-benchmark.md
@@ -22,8 +22,8 @@ Finally, we extrapolate performance projections for upcoming GPUs like NVIDIA H2
@@ -80,7 +80,7 @@ Workflows became standardized, reproducible, and easier to trace—thanks to the
By adopting tools that are cloud-agnostic and developer-friendly, EA has reduced friction—from provisioning GPUs to deploying models—and enabled teams to spend more time on actual ML work.
-*Huge thanks to Kris and Keng from EA’s central tech team for sharing these insights. For more details, including the recording and slides, check out the full talk on the [NVIDIA GTC website :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://www.nvidia.com/en-us/on-demand/session/gtc25-s73667/){:target="_blank"}.*
+*Huge thanks to Kris and Keng from EA’s central tech team for sharing these insights. For more details, including the recording and slides, check out the full talk on the [NVIDIA GTC website](https://www.nvidia.com/en-us/on-demand/session/gtc25-s73667/).*
!!! info "What's next?"
1. Check [dev environments](../../docs/concepts/dev-environments.md), [tasks](../../docs/concepts/tasks.md), [services](../../docs/concepts/services.md), and [fleets](../../docs/concepts/fleets.md)
diff --git a/docs/blog/posts/gh200-on-lambda.md b/docs/blog/posts/gh200-on-lambda.md
index e7831a76c..1a87dc90e 100644
--- a/docs/blog/posts/gh200-on-lambda.md
+++ b/docs/blog/posts/gh200-on-lambda.md
@@ -42,7 +42,7 @@ The GH200 Superchip’s 450 GB/s bidirectional bandwidth enables KV cache offloa
## GH200 on Lambda
-[Lambda :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://cloud.lambda.ai/sign-up?_gl=1*1qovk06*_gcl_au*MTg2MDc3OTAyOS4xNzQyOTA3Nzc0LjE3NDkwNTYzNTYuMTc0NTQxOTE2MS4xNzQ1NDE5MTYw*_ga*MTE2NDM5MzI0My4xNzQyOTA3Nzc0*_ga_43EZT1FM6Q*czE3NDY3MTczOTYkbzM0JGcxJHQxNzQ2NzE4MDU2JGo1NyRsMCRoMTU0Mzg1NTU1OQ..){:target="_blank"} provides secure, user-friendly, reliable, and affordable cloud GPUs. Since end of last year, Lambda started to offer on-demand GH200 instances through their public cloud. Furthermore, they offer these instances at the promotional price of $1.49 per hour until June 30th 2025.
+[Lambda](https://cloud.lambda.ai/sign-up?_gl=1*1qovk06*_gcl_au*MTg2MDc3OTAyOS4xNzQyOTA3Nzc0LjE3NDkwNTYzNTYuMTc0NTQxOTE2MS4xNzQ1NDE5MTYw*_ga*MTE2NDM5MzI0My4xNzQyOTA3Nzc0*_ga_43EZT1FM6Q*czE3NDY3MTczOTYkbzM0JGcxJHQxNzQ2NzE4MDU2JGo1NyRsMCRoMTU0Mzg1NTU1OQ..) provides secure, user-friendly, reliable, and affordable cloud GPUs. Since end of last year, Lambda started to offer on-demand GH200 instances through their public cloud. Furthermore, they offer these instances at the promotional price of $1.49 per hour until June 30th 2025.
With the latest `dstack` update, it’s now possible to use these instances with your Lambda account whether you’re running a dev environment, task, or service:
@@ -81,7 +81,7 @@ $ dstack apply -f .dstack.yml
> If you have GH200 or GB200-powered hosts already provisioned via Lambda, another cloud provider, or on-prem, you can now use them with [SSH fleets](../../docs/concepts/fleets.md#ssh-fleets).
!!! info "What's next?"
- 1. Sign up with [Lambda :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://cloud.lambda.ai/sign-up?_gl=1*1qovk06*_gcl_au*MTg2MDc3OTAyOS4xNzQyOTA3Nzc0LjE3NDkwNTYzNTYuMTc0NTQxOTE2MS4xNzQ1NDE5MTYw*_ga*MTE2NDM5MzI0My4xNzQyOTA3Nzc0*_ga_43EZT1FM6Q*czE3NDY3MTczOTYkbzM0JGcxJHQxNzQ2NzE4MDU2JGo1NyRsMCRoMTU0Mzg1NTU1OQ..){:target="_blank"}
+ 1. Sign up with [Lambda](https://cloud.lambda.ai/sign-up?_gl=1*1qovk06*_gcl_au*MTg2MDc3OTAyOS4xNzQyOTA3Nzc0LjE3NDkwNTYzNTYuMTc0NTQxOTE2MS4xNzQ1NDE5MTYw*_ga*MTE2NDM5MzI0My4xNzQyOTA3Nzc0*_ga_43EZT1FM6Q*czE3NDY3MTczOTYkbzM0JGcxJHQxNzQ2NzE4MDU2JGo1NyRsMCRoMTU0Mzg1NTU1OQ..)
2. Set up the [Lambda](../../docs/concepts/backends.md#lambda) backend
3. Follow [Quickstart](../../docs/quickstart.md)
4. Check [dev environments](../../docs/concepts/dev-environments.md), [tasks](../../docs/concepts/tasks.md), [services](../../docs/concepts/services.md), and [fleets](../../docs/concepts/fleets.md)
diff --git a/docs/blog/posts/gpu-blocks-and-proxy-jump.md b/docs/blog/posts/gpu-blocks-and-proxy-jump.md
index cbf9ab7dc..61f28ea81 100644
--- a/docs/blog/posts/gpu-blocks-and-proxy-jump.md
+++ b/docs/blog/posts/gpu-blocks-and-proxy-jump.md
@@ -39,7 +39,7 @@ enables optimal hardware utilization by allowing concurrent workloads to run on
available resources on each host.
> For example, imagine you’ve reserved a cluster with multiple bare-metal nodes, each equipped with 8x MI300X GPUs from
-[Hot Aisle :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://hotaisle.xyz/){:target="_blank"}.
+[Hot Aisle](https://hotaisle.xyz/).
With `dstack`, you can define your fleet configuration like this:
@@ -108,7 +108,7 @@ The latest `dstack` release introduces the [`proxy_jump`](../../docs/concepts/fl
through a login node.
> For example, imagine you’ve reserved a 1-Click Cluster from
-> [Lambda :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://lambdalabs.com/){:target="_blank"} with multiple nodes, each equipped with 8x H100 GPUs from.
+> [Lambda](https://lambdalabs.com/) with multiple nodes, each equipped with 8x H100 GPUs from.
With `dstack`, you can define your fleet configuration like this:
@@ -174,8 +174,8 @@ an AI-native experience, simplicity, and vendor-agnostic orchestration for both
!!! info "Roadmap"
We plan to further enhance `dstack`'s support for both cloud and on-premises setups. For more details on our roadmap,
- refer to our [GitHub :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://github.com/dstackai/dstack/issues/2184){:target="_blank"}.
+ refer to our [GitHub](https://github.com/dstackai/dstack/issues/2184).
> Have questions? You're welcome to join
-> our [Discord :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://discord.gg/u8SmfwPpMd){:target="_blank"} or talk
-> directly to [our team :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://calendly.com/dstackai/discovery-call){:target="_blank"}.
+> our [Discord](https://discord.gg/u8SmfwPpMd) or talk
+> directly to [our team](https://calendly.com/dstackai/discovery-call).
diff --git a/docs/blog/posts/gpu-health-checks.md b/docs/blog/posts/gpu-health-checks.md
index 1571935b6..cc28bb96a 100644
--- a/docs/blog/posts/gpu-health-checks.md
+++ b/docs/blog/posts/gpu-health-checks.md
@@ -64,10 +64,10 @@ Passive GPU health checks work on AWS (except with custom `os_images`), Azure (e
This update is about visibility: giving engineers real-time insight into GPU health before jobs run. Next comes automation — policies to skip GPUs with warnings, and self-healing workflows that replace unhealthy instances without manual steps.
If you have experience with GPU reliability or ideas for automated recovery, join the conversation on
-[Discord :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://discord.gg/u8SmfwPpMd){:target="_blank"}.
+[Discord](https://discord.gg/u8SmfwPpMd).
!!! info "What's next?"
1. Check [Quickstart](../../docs/quickstart.md)
2. Explore the [clusters](../../docs/guides/clusters.md) guide
3. Learn more about [metrics](../../docs/guides/metrics.md)
- 4. Join [Discord :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://discord.gg/u8SmfwPpMd){:target="_blank"}
+ 4. Join [Discord](https://discord.gg/u8SmfwPpMd)
diff --git a/docs/blog/posts/h100-mi300x-inference-benchmark.md b/docs/blog/posts/h100-mi300x-inference-benchmark.md
index 350795684..2209393d1 100644
--- a/docs/blog/posts/h100-mi300x-inference-benchmark.md
+++ b/docs/blog/posts/h100-mi300x-inference-benchmark.md
@@ -22,8 +22,8 @@ Finally, we extrapolate performance projections for upcoming GPUs like NVIDIA H2
 This benchmark is made possible through the generous support of our friends at
-[Hot Aisle :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://hotaisle.xyz/){:target="_blank"} and
-[Lambda :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://lambdalabs.com/){:target="_blank"},
+[Hot Aisle](https://hotaisle.xyz/) and
+[Lambda](https://lambdalabs.com/),
who provided high-end hardware.
@@ -42,7 +42,7 @@ who provided high-end hardware.
### Benchmark modes
1. **Online inference**: Benchmarked across QPS 16, 32, and 1000 using
- the [ShareGPT :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://huggingface.co/datasets/anon8231489123/ShareGPT_Vicuna_unfiltered){:target="_blank"} dataset. Execution used
+ the [ShareGPT](https://huggingface.co/datasets/anon8231489123/ShareGPT_Vicuna_unfiltered) dataset. Execution used
vLLM’s [benchmark\_serving](https://github.com/vllm-project/vllm/blob/main/benchmarks/benchmark_serving.py).
2. **Offline inference**: Benchmarked with varying input/output lengths across different batch sizes, using vLLM’s [benchmark\_throughput.py](https://github.com/vllm-project/vllm/blob/main/benchmarks/benchmark_throughput.py).
@@ -79,7 +79,7 @@ With large prompts and batch sizes, two replicas on 4xMI300x GPUs hit memory sat
length x batch size) exceed the available memory for the KV cache. This forces the inference engine to compute KV
tensors on-the-fly or offload them to CPU memory, degrading throughput.
-In [Lambda :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://lambdalabs.com/blog/partner-spotlight-evaluating-nvidia-h200-gpus-for-ai-inference-with-baseten){:target="_blank"}’
+In [Lambda](https://lambdalabs.com/blog/partner-spotlight-evaluating-nvidia-h200-gpus-for-ai-inference-with-baseten)’
benchmark, an 8xH200 setup processed 3.4 times more tokens per second than an 8xH100. Extrapolating to our
setup, an 8xH200 would process around 2,186 tokens per second (3.4 × 643), though still lower than 8xMI300x.
@@ -122,7 +122,7 @@ Despite offering more memory, 4xMI300x lacks the parallelism of 8xH100, leading
Processing a single large prompt request with 8xMI300x takes around 11.25 seconds. This latency is mainly due to
computational demands during the prefill phase, where KV tensors are computed.
-Optimizations like [automatic prefix caching :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://docs.vllm.ai/en/latest/automatic_prefix_caching/apc.html){:target="_blank"}
+Optimizations like [automatic prefix caching](https://docs.vllm.ai/en/latest/automatic_prefix_caching/apc.html)
could help reduce this time, but are outside the scope of this benchmark.
## Benchmark notes
@@ -139,7 +139,7 @@ with batch size 16 due to memory saturation, resulting in slower generation time
### Model checkpoints
-For AMD MI300x, we used [`amd/Llama-3.1-405B-Instruct-FP8-KV` :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://huggingface.co/amd/Llama-3.1-405B-Instruct-FP8-KV){:target="_blank"}
+For AMD MI300x, we used [`amd/Llama-3.1-405B-Instruct-FP8-KV`](https://huggingface.co/amd/Llama-3.1-405B-Instruct-FP8-KV)
to achieve optimal performance, relying on AMD for quantization.
### vLLM configuration
@@ -186,20 +186,20 @@ cost-efficiency.
## Source code
All the source code and findings to help you replicate the results are available in
-[our GitHub repo :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://github.com/dstackai/benchmarks/tree/main/comparison/h100sxm5_vs_mi300x){:target="_blank"}.
+[our GitHub repo](https://github.com/dstackai/benchmarks/tree/main/comparison/h100sxm5_vs_mi300x).
## Thanks to our friends
### Hot Aisle
-[Hot Aisle :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://hotaisle.xyz/){:target="_blank"} sponsored this benchmark by providing access to 8x MI300x hardware. We’re deeply grateful for their support.
+[Hot Aisle](https://hotaisle.xyz/) sponsored this benchmark by providing access to 8x MI300x hardware. We’re deeply grateful for their support.
If you're looking for top-tier bare metal compute with AMD GPUs, we highly recommend Hot Aisle. With `dstack`, accessing
your cluster via SSH is seamless and straightforward.
### Lambda
-[Lambda :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://lambdalabs.com/){:target="_blank"} sponsored this benchmark with credits for on-demand 8x H100 instances.
+[Lambda](https://lambdalabs.com/) sponsored this benchmark with credits for on-demand 8x H100 instances.
We’re truly thankful for their support.
For top-tier cloud compute with NVIDIA GPUs, Lambda is an excellent choice. Once set up, you can easily provision
diff --git a/docs/blog/posts/h200-mi300x-deepskeek-benchmark.md b/docs/blog/posts/h200-mi300x-deepskeek-benchmark.md
index 0d9e6f1fe..b8587d43f 100644
--- a/docs/blog/posts/h200-mi300x-deepskeek-benchmark.md
+++ b/docs/blog/posts/h200-mi300x-deepskeek-benchmark.md
@@ -21,8 +21,8 @@ determine the optimal backend and hardware pairing for DeepSeek-R1's demanding r
This benchmark is made possible through the generous support of our friends at
-[Hot Aisle :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://hotaisle.xyz/){:target="_blank"} and
-[Lambda :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://lambdalabs.com/){:target="_blank"},
+[Hot Aisle](https://hotaisle.xyz/) and
+[Lambda](https://lambdalabs.com/),
who provided high-end hardware.
@@ -42,7 +42,7 @@ who provided high-end hardware.
### Benchmark modes
1. **Online inference**: Benchmarked across QPS 16, 32, and 1000 using
- the [ShareGPT :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://huggingface.co/datasets/anon8231489123/ShareGPT_Vicuna_unfiltered){:target="_blank"} dataset. Execution used
+ the [ShareGPT](https://huggingface.co/datasets/anon8231489123/ShareGPT_Vicuna_unfiltered) dataset. Execution used
vLLM’s [benchmark\_serving](https://github.com/vllm-project/vllm/blob/main/benchmarks/benchmark_serving.py).
2. **Offline inference**: Benchmarked with varying input/output lengths across different batch sizes, using vLLM’s [benchmark\_throughput.py](https://github.com/vllm-project/vllm/blob/main/benchmarks/benchmark_throughput.py).
@@ -79,7 +79,7 @@ With large prompts and batch sizes, two replicas on 4xMI300x GPUs hit memory sat
length x batch size) exceed the available memory for the KV cache. This forces the inference engine to compute KV
tensors on-the-fly or offload them to CPU memory, degrading throughput.
-In [Lambda :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://lambdalabs.com/blog/partner-spotlight-evaluating-nvidia-h200-gpus-for-ai-inference-with-baseten){:target="_blank"}’
+In [Lambda](https://lambdalabs.com/blog/partner-spotlight-evaluating-nvidia-h200-gpus-for-ai-inference-with-baseten)’
benchmark, an 8xH200 setup processed 3.4 times more tokens per second than an 8xH100. Extrapolating to our
setup, an 8xH200 would process around 2,186 tokens per second (3.4 × 643), though still lower than 8xMI300x.
@@ -122,7 +122,7 @@ Despite offering more memory, 4xMI300x lacks the parallelism of 8xH100, leading
Processing a single large prompt request with 8xMI300x takes around 11.25 seconds. This latency is mainly due to
computational demands during the prefill phase, where KV tensors are computed.
-Optimizations like [automatic prefix caching :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://docs.vllm.ai/en/latest/automatic_prefix_caching/apc.html){:target="_blank"}
+Optimizations like [automatic prefix caching](https://docs.vllm.ai/en/latest/automatic_prefix_caching/apc.html)
could help reduce this time, but are outside the scope of this benchmark.
## Benchmark notes
@@ -139,7 +139,7 @@ with batch size 16 due to memory saturation, resulting in slower generation time
### Model checkpoints
-For AMD MI300x, we used [`amd/Llama-3.1-405B-Instruct-FP8-KV` :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://huggingface.co/amd/Llama-3.1-405B-Instruct-FP8-KV){:target="_blank"}
+For AMD MI300x, we used [`amd/Llama-3.1-405B-Instruct-FP8-KV`](https://huggingface.co/amd/Llama-3.1-405B-Instruct-FP8-KV)
to achieve optimal performance, relying on AMD for quantization.
### vLLM configuration
@@ -186,20 +186,20 @@ cost-efficiency.
## Source code
All the source code and findings to help you replicate the results are available in
-[our GitHub repo :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://github.com/dstackai/benchmarks/tree/main/comparison/h100sxm5_vs_mi300x){:target="_blank"}.
+[our GitHub repo](https://github.com/dstackai/benchmarks/tree/main/comparison/h100sxm5_vs_mi300x).
## Thanks to our friends
### Hot Aisle
-[Hot Aisle :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://hotaisle.xyz/){:target="_blank"} sponsored this benchmark by providing access to 8x MI300x hardware. We’re deeply grateful for their support.
+[Hot Aisle](https://hotaisle.xyz/) sponsored this benchmark by providing access to 8x MI300x hardware. We’re deeply grateful for their support.
If you're looking for top-tier bare metal compute with AMD GPUs, we highly recommend Hot Aisle. With `dstack`, accessing
your cluster via SSH is seamless and straightforward.
### Lambda
-[Lambda :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://lambdalabs.com/){:target="_blank"} sponsored this benchmark with credits for on-demand 8x H100 instances.
+[Lambda](https://lambdalabs.com/) sponsored this benchmark with credits for on-demand 8x H100 instances.
We’re truly thankful for their support.
For top-tier cloud compute with NVIDIA GPUs, Lambda is an excellent choice. Once set up, you can easily provision
diff --git a/docs/blog/posts/h200-mi300x-deepskeek-benchmark.md b/docs/blog/posts/h200-mi300x-deepskeek-benchmark.md
index 0d9e6f1fe..b8587d43f 100644
--- a/docs/blog/posts/h200-mi300x-deepskeek-benchmark.md
+++ b/docs/blog/posts/h200-mi300x-deepskeek-benchmark.md
@@ -21,8 +21,8 @@ determine the optimal backend and hardware pairing for DeepSeek-R1's demanding r
 This benchmark was made possible through the generous support of our partners at
-[Vultr :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://www.vultr.com/){:target="_blank"} and
-[Lambda :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://lambdalabs.com/){:target="_blank"},
+[Vultr](https://www.vultr.com/) and
+[Lambda](https://lambdalabs.com/),
who provided access to the necessary hardware.
@@ -44,7 +44,7 @@ who provided access to the necessary hardware.
**Online inference**
-We utilized SGLang's [`Deepseek-R1/bench_serving.py` :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://github.com/dstackai/benchmarks/tree/main/Deepseek-R1/bench_serving.py){:target="_blank"}
+We utilized SGLang's [`Deepseek-R1/bench_serving.py`](https://github.com/dstackai/benchmarks/tree/main/Deepseek-R1/bench_serving.py)
script, modified to incorporate TensorRT-LLM.
Tests were conducted across multiple request concurrencies and output token lengths, with input token length fixed at 3200.
@@ -59,9 +59,9 @@ To test prefix caching ability, about 62.5% of each ~3200-token prompt (i.e., 20
**Offline inference**
-For offline inference, we used vLLM’s [`benchmark_throughput.py` :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://github.com/vllm-project/vllm/blob/main/benchmarks/benchmark_throughput.py){:target="_blank"},
+For offline inference, we used vLLM’s [`benchmark_throughput.py`](https://github.com/vllm-project/vllm/blob/main/benchmarks/benchmark_throughput.py),
modified for SGLang. TensorRT-LLM was tested using a custom
-[`benchmark_throughput_trt.py` :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://github.com/dstackai/benchmarks/blob/deepseek-r1-benchmark/Deepseek-R1/benchmark_throughput_trt.py){:target="_blank"}.
+[`benchmark_throughput_trt.py`](https://github.com/dstackai/benchmarks/blob/deepseek-r1-benchmark/Deepseek-R1/benchmark_throughput_trt.py).
The benchmark examined performance across various batch sizes and output token lengths.
| Batch Sizes | Output Token Lengths |
@@ -129,7 +129,7 @@ TensorRT-LLM maintained the lowest and most consistent TTFT up to concurrency 64
vLLM achieved the lowest TTFT at concurrency 128. Below 128, vLLM and SGLang had similar TTFT.
-TTFT, being compute-intensive, highlights H200's advantage, aligning with [SemiAnalysis’s MI300X vs. H200 TFLOPS benchmark :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://semianalysis.com/2024/12/22/mi300x-vs-h100-vs-h200-benchmark-part-1-training/){:target="_blank"}.
+TTFT, being compute-intensive, highlights H200's advantage, aligning with [SemiAnalysis’s MI300X vs. H200 TFLOPS benchmark](https://semianalysis.com/2024/12/22/mi300x-vs-h100-vs-h200-benchmark-part-1-training/).
However, at 128 concurrent requests, MI300X's memory capacity and bandwidth advantages become evident.
### Time Per Output Token (TPOT)
@@ -194,10 +194,10 @@ TPOT increased after prefix caching, which requires further investigation.
## Limitations
1. The offline benchmark results for TensorRT-LLM were obtained using the DeepSeek-R1 model engine built from the
- [`deepseek` branch :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://github.com/NVIDIA/TensorRT-LLM/tree/deepseek){:target="_blank"}.
+ [`deepseek` branch](https://github.com/NVIDIA/TensorRT-LLM/tree/deepseek).
However, the TensorRT-LLM team recommends using the TorchFlow-based approach for deployment.
2. The impact of dynamic batching on inference efficiency was not tested.
-3. vLLM's prefix caching support for MI300X is a work in progress and can be tracked [here :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://github.com/ROCm/vllm/issues/457){:target="_blank"}.
+3. vLLM's prefix caching support for MI300X is a work in progress and can be tracked [here](https://github.com/ROCm/vllm/issues/457).
4. The inference backends are being optimized for the DeepSeek-R1 model. Given these continuous updates, the current
results reflect only the performance tested at the time of the benchmark. Overall, performance for all backends is
expected to improve as more optimizations are made by the backend teams.
@@ -205,27 +205,27 @@ TPOT increased after prefix caching, which requires further investigation.
## Source code
All source code and findings are available in
-[our GitHub repo :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://github.com/dstackai/benchmarks/tree/deepseek-r1-benchmark/Deepseek-R1){:target="_blank"}.
+[our GitHub repo](https://github.com/dstackai/benchmarks/tree/deepseek-r1-benchmark/Deepseek-R1).
## References
-* [Unlock DeepSeek-R1 Inference Performance on AMD Instinct MI300X GPU :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://rocm.blogs.amd.com/artificial-intelligence/DeepSeekR1_Perf/README.html){:target="_blank"}
-* [Deploy DeepSeek-R1 671B on 8x NVIDIA H200 with SGLang :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://datacrunch.io/blog/deploy-deepseek-r1-on-8x-nvidia-h200){:target="_blank"}
-* [vLLM Prefix Caching :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://docs.vllm.ai/en/latest/design/automatic_prefix_caching.html#design-automatic-prefix-caching){:target="_blank"}
-* [SgLang Prefix Caching :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://lmsys.org/blog/2024-01-17-sglang/){:target="_blank"}
+* [Unlock DeepSeek-R1 Inference Performance on AMD Instinct MI300X GPU](https://rocm.blogs.amd.com/artificial-intelligence/DeepSeekR1_Perf/README.html)
+* [Deploy DeepSeek-R1 671B on 8x NVIDIA H200 with SGLang](https://datacrunch.io/blog/deploy-deepseek-r1-on-8x-nvidia-h200)
+* [vLLM Prefix Caching](https://docs.vllm.ai/en/latest/design/automatic_prefix_caching.html#design-automatic-prefix-caching)
+* [SgLang Prefix Caching](https://lmsys.org/blog/2024-01-17-sglang/)
## Acknowledgments
### Vultr
-[Vultr :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://www.vultr.com/){:target="_blank"} provided access to 8x AMD MI300X GPUs. We are truly thankful for their support.
+[Vultr](https://www.vultr.com/) provided access to 8x AMD MI300X GPUs. We are truly thankful for their support.
If you're looking for top-tier bare metal compute with AMD GPUs, we highly recommend Vultr. With `dstack`, provisioning
and accessing compute via `dstack` is seamless and straightforward.
### Lambda
-[Lambda :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://lambdalabs.com/){:target="_blank"} provided access to 8x
+[Lambda](https://lambdalabs.com/) provided access to 8x
NVIDIA H200 GPUs. We are truly thankful for their support
Both Vultr and Lambda are natively supported and can be seamlessly integrated with `dstack`.
diff --git a/docs/blog/posts/hotaisle.md b/docs/blog/posts/hotaisle.md
index 4d2e761c0..928d0cf9c 100644
--- a/docs/blog/posts/hotaisle.md
+++ b/docs/blog/posts/hotaisle.md
@@ -16,7 +16,7 @@ As the ecosystem around AMD GPUs matures, developers are looking for easier ways
This benchmark was made possible through the generous support of our partners at
-[Vultr :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://www.vultr.com/){:target="_blank"} and
-[Lambda :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://lambdalabs.com/){:target="_blank"},
+[Vultr](https://www.vultr.com/) and
+[Lambda](https://lambdalabs.com/),
who provided access to the necessary hardware.
@@ -44,7 +44,7 @@ who provided access to the necessary hardware.
**Online inference**
-We utilized SGLang's [`Deepseek-R1/bench_serving.py` :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://github.com/dstackai/benchmarks/tree/main/Deepseek-R1/bench_serving.py){:target="_blank"}
+We utilized SGLang's [`Deepseek-R1/bench_serving.py`](https://github.com/dstackai/benchmarks/tree/main/Deepseek-R1/bench_serving.py)
script, modified to incorporate TensorRT-LLM.
Tests were conducted across multiple request concurrencies and output token lengths, with input token length fixed at 3200.
@@ -59,9 +59,9 @@ To test prefix caching ability, about 62.5% of each ~3200-token prompt (i.e., 20
**Offline inference**
-For offline inference, we used vLLM’s [`benchmark_throughput.py` :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://github.com/vllm-project/vllm/blob/main/benchmarks/benchmark_throughput.py){:target="_blank"},
+For offline inference, we used vLLM’s [`benchmark_throughput.py`](https://github.com/vllm-project/vllm/blob/main/benchmarks/benchmark_throughput.py),
modified for SGLang. TensorRT-LLM was tested using a custom
-[`benchmark_throughput_trt.py` :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://github.com/dstackai/benchmarks/blob/deepseek-r1-benchmark/Deepseek-R1/benchmark_throughput_trt.py){:target="_blank"}.
+[`benchmark_throughput_trt.py`](https://github.com/dstackai/benchmarks/blob/deepseek-r1-benchmark/Deepseek-R1/benchmark_throughput_trt.py).
The benchmark examined performance across various batch sizes and output token lengths.
| Batch Sizes | Output Token Lengths |
@@ -129,7 +129,7 @@ TensorRT-LLM maintained the lowest and most consistent TTFT up to concurrency 64
vLLM achieved the lowest TTFT at concurrency 128. Below 128, vLLM and SGLang had similar TTFT.
-TTFT, being compute-intensive, highlights H200's advantage, aligning with [SemiAnalysis’s MI300X vs. H200 TFLOPS benchmark :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://semianalysis.com/2024/12/22/mi300x-vs-h100-vs-h200-benchmark-part-1-training/){:target="_blank"}.
+TTFT, being compute-intensive, highlights H200's advantage, aligning with [SemiAnalysis’s MI300X vs. H200 TFLOPS benchmark](https://semianalysis.com/2024/12/22/mi300x-vs-h100-vs-h200-benchmark-part-1-training/).
However, at 128 concurrent requests, MI300X's memory capacity and bandwidth advantages become evident.
### Time Per Output Token (TPOT)
@@ -194,10 +194,10 @@ TPOT increased after prefix caching, which requires further investigation.
## Limitations
1. The offline benchmark results for TensorRT-LLM were obtained using the DeepSeek-R1 model engine built from the
- [`deepseek` branch :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://github.com/NVIDIA/TensorRT-LLM/tree/deepseek){:target="_blank"}.
+ [`deepseek` branch](https://github.com/NVIDIA/TensorRT-LLM/tree/deepseek).
However, the TensorRT-LLM team recommends using the TorchFlow-based approach for deployment.
2. The impact of dynamic batching on inference efficiency was not tested.
-3. vLLM's prefix caching support for MI300X is a work in progress and can be tracked [here :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://github.com/ROCm/vllm/issues/457){:target="_blank"}.
+3. vLLM's prefix caching support for MI300X is a work in progress and can be tracked [here](https://github.com/ROCm/vllm/issues/457).
4. The inference backends are being optimized for the DeepSeek-R1 model. Given these continuous updates, the current
results reflect only the performance tested at the time of the benchmark. Overall, performance for all backends is
expected to improve as more optimizations are made by the backend teams.
@@ -205,27 +205,27 @@ TPOT increased after prefix caching, which requires further investigation.
## Source code
All source code and findings are available in
-[our GitHub repo :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://github.com/dstackai/benchmarks/tree/deepseek-r1-benchmark/Deepseek-R1){:target="_blank"}.
+[our GitHub repo](https://github.com/dstackai/benchmarks/tree/deepseek-r1-benchmark/Deepseek-R1).
## References
-* [Unlock DeepSeek-R1 Inference Performance on AMD Instinct MI300X GPU :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://rocm.blogs.amd.com/artificial-intelligence/DeepSeekR1_Perf/README.html){:target="_blank"}
-* [Deploy DeepSeek-R1 671B on 8x NVIDIA H200 with SGLang :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://datacrunch.io/blog/deploy-deepseek-r1-on-8x-nvidia-h200){:target="_blank"}
-* [vLLM Prefix Caching :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://docs.vllm.ai/en/latest/design/automatic_prefix_caching.html#design-automatic-prefix-caching){:target="_blank"}
-* [SgLang Prefix Caching :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://lmsys.org/blog/2024-01-17-sglang/){:target="_blank"}
+* [Unlock DeepSeek-R1 Inference Performance on AMD Instinct MI300X GPU](https://rocm.blogs.amd.com/artificial-intelligence/DeepSeekR1_Perf/README.html)
+* [Deploy DeepSeek-R1 671B on 8x NVIDIA H200 with SGLang](https://datacrunch.io/blog/deploy-deepseek-r1-on-8x-nvidia-h200)
+* [vLLM Prefix Caching](https://docs.vllm.ai/en/latest/design/automatic_prefix_caching.html#design-automatic-prefix-caching)
+* [SgLang Prefix Caching](https://lmsys.org/blog/2024-01-17-sglang/)
## Acknowledgments
### Vultr
-[Vultr :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://www.vultr.com/){:target="_blank"} provided access to 8x AMD MI300X GPUs. We are truly thankful for their support.
+[Vultr](https://www.vultr.com/) provided access to 8x AMD MI300X GPUs. We are truly thankful for their support.
If you're looking for top-tier bare metal compute with AMD GPUs, we highly recommend Vultr. With `dstack`, provisioning
and accessing compute via `dstack` is seamless and straightforward.
### Lambda
-[Lambda :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://lambdalabs.com/){:target="_blank"} provided access to 8x
+[Lambda](https://lambdalabs.com/) provided access to 8x
NVIDIA H200 GPUs. We are truly thankful for their support
Both Vultr and Lambda are natively supported and can be seamlessly integrated with `dstack`.
diff --git a/docs/blog/posts/hotaisle.md b/docs/blog/posts/hotaisle.md
index 4d2e761c0..928d0cf9c 100644
--- a/docs/blog/posts/hotaisle.md
+++ b/docs/blog/posts/hotaisle.md
@@ -16,7 +16,7 @@ As the ecosystem around AMD GPUs matures, developers are looking for easier ways
 -Today, we’re excited to announce native integration with [Hot Aisle :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://www.hotaisle.io/){:target="_blank"}, an AMD-only GPU neocloud offering VMs and clusters at highly competitive on-demand pricing.
+Today, we’re excited to announce native integration with [Hot Aisle](https://www.hotaisle.io/), an AMD-only GPU neocloud offering VMs and clusters at highly competitive on-demand pricing.
@@ -107,8 +107,8 @@ Currently, `dstack` supports 1xGPU Hot Aisle VMs. Support for 8xGPU VMs will be
!!! info "What's next?"
1. Check [Quickstart](../../docs/quickstart.md)
- 2. Learn more about [Hot Aisle :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://hotaisle.xyz/){:target="_blank"}
+ 2. Learn more about [Hot Aisle](https://hotaisle.xyz/)
3. Explore [dev environments](../../docs/concepts/dev-environments.md),
[tasks](../../docs/concepts/tasks.md), [services](../../docs/concepts/services.md),
and [fleets](../../docs/concepts/fleets.md)
- 4. Join [Discord :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://discord.gg/u8SmfwPpMd){:target="_blank"}
+ 4. Join [Discord](https://discord.gg/u8SmfwPpMd)
diff --git a/docs/blog/posts/inactivity-duration.md b/docs/blog/posts/inactivity-duration.md
index d04a8eba4..7c3d88eb5 100644
--- a/docs/blog/posts/inactivity-duration.md
+++ b/docs/blog/posts/inactivity-duration.md
@@ -72,4 +72,4 @@ fleets by teams.
1. Check [dev environments](../../docs/concepts/dev-environments.md),
[tasks](../../docs/concepts/tasks.md), [services](../../docs/concepts/services.md),
and [fleets](../../docs/concepts/fleets.md)
- 2. Join [Discord :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://discord.gg/u8SmfwPpMd){:target="_blank"}
+ 2. Join [Discord](https://discord.gg/u8SmfwPpMd)
diff --git a/docs/blog/posts/instance-volumes.md b/docs/blog/posts/instance-volumes.md
index 07b82012c..36ead6930 100644
--- a/docs/blog/posts/instance-volumes.md
+++ b/docs/blog/posts/instance-volumes.md
@@ -82,6 +82,6 @@ volumes:
## Feedback
If you find something not working as intended, please be sure to report it to
-[GitHub issues :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://github.com/dstackai/dstack/issues){:target="_ blank"}.
+[GitHub issues](https://github.com/dstackai/dstack/issues){:target="_ blank"}.
Your feedback and feature requests is also very welcome on our
-[Discord :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://discord.gg/u8SmfwPpMd){:target="_blank"} server.
+[Discord](https://discord.gg/u8SmfwPpMd) server.
diff --git a/docs/blog/posts/intel-gaudi.md b/docs/blog/posts/intel-gaudi.md
index 887ae32a6..4ac0e6770 100644
--- a/docs/blog/posts/intel-gaudi.md
+++ b/docs/blog/posts/intel-gaudi.md
@@ -92,10 +92,10 @@ Provisioning...
With your fleet provisioned, you can now run [dev environments](../../docs/concepts/dev-environments.md), [tasks](../../docs/concepts/tasks.md), [services](../../docs/concepts/services.md).
-Below is an example of a task configuration for fine-tuning the [`DeepSeek-R1-Distill-Qwen-7B` :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://huggingface.co/deepseek-ai/DeepSeek-R1-Distill-Qwen-7B){:target="_blank"}
-model using [Optimum for Intel Gaudi :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://github.com/huggingface/optimum-habana){:target="_blank"}
-and [DeepSpeed :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://docs.habana.ai/en/latest/PyTorch/DeepSpeed/DeepSpeed_User_Guide/DeepSpeed_User_Guide.html#deepspeed-user-guide){:target="_blank"} with
-the [`lvwerra/stack-exchange-paired` :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://huggingface.co/datasets/lvwerra/stack-exchange-paired){:target="_blank"} dataset:
+Below is an example of a task configuration for fine-tuning the [`DeepSeek-R1-Distill-Qwen-7B`](https://huggingface.co/deepseek-ai/DeepSeek-R1-Distill-Qwen-7B)
+model using [Optimum for Intel Gaudi](https://github.com/huggingface/optimum-habana)
+and [DeepSpeed](https://docs.habana.ai/en/latest/PyTorch/DeepSpeed/DeepSpeed_User_Guide/DeepSpeed_User_Guide.html#deepspeed-user-guide) with
+the [`lvwerra/stack-exchange-paired`](https://huggingface.co/datasets/lvwerra/stack-exchange-paired) dataset:
-Today, we’re excited to announce native integration with [Hot Aisle :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://www.hotaisle.io/){:target="_blank"}, an AMD-only GPU neocloud offering VMs and clusters at highly competitive on-demand pricing.
+Today, we’re excited to announce native integration with [Hot Aisle](https://www.hotaisle.io/), an AMD-only GPU neocloud offering VMs and clusters at highly competitive on-demand pricing.
@@ -107,8 +107,8 @@ Currently, `dstack` supports 1xGPU Hot Aisle VMs. Support for 8xGPU VMs will be
!!! info "What's next?"
1. Check [Quickstart](../../docs/quickstart.md)
- 2. Learn more about [Hot Aisle :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://hotaisle.xyz/){:target="_blank"}
+ 2. Learn more about [Hot Aisle](https://hotaisle.xyz/)
3. Explore [dev environments](../../docs/concepts/dev-environments.md),
[tasks](../../docs/concepts/tasks.md), [services](../../docs/concepts/services.md),
and [fleets](../../docs/concepts/fleets.md)
- 4. Join [Discord :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://discord.gg/u8SmfwPpMd){:target="_blank"}
+ 4. Join [Discord](https://discord.gg/u8SmfwPpMd)
diff --git a/docs/blog/posts/inactivity-duration.md b/docs/blog/posts/inactivity-duration.md
index d04a8eba4..7c3d88eb5 100644
--- a/docs/blog/posts/inactivity-duration.md
+++ b/docs/blog/posts/inactivity-duration.md
@@ -72,4 +72,4 @@ fleets by teams.
1. Check [dev environments](../../docs/concepts/dev-environments.md),
[tasks](../../docs/concepts/tasks.md), [services](../../docs/concepts/services.md),
and [fleets](../../docs/concepts/fleets.md)
- 2. Join [Discord :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://discord.gg/u8SmfwPpMd){:target="_blank"}
+ 2. Join [Discord](https://discord.gg/u8SmfwPpMd)
diff --git a/docs/blog/posts/instance-volumes.md b/docs/blog/posts/instance-volumes.md
index 07b82012c..36ead6930 100644
--- a/docs/blog/posts/instance-volumes.md
+++ b/docs/blog/posts/instance-volumes.md
@@ -82,6 +82,6 @@ volumes:
## Feedback
If you find something not working as intended, please be sure to report it to
-[GitHub issues :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://github.com/dstackai/dstack/issues){:target="_ blank"}.
+[GitHub issues](https://github.com/dstackai/dstack/issues){:target="_ blank"}.
Your feedback and feature requests is also very welcome on our
-[Discord :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://discord.gg/u8SmfwPpMd){:target="_blank"} server.
+[Discord](https://discord.gg/u8SmfwPpMd) server.
diff --git a/docs/blog/posts/intel-gaudi.md b/docs/blog/posts/intel-gaudi.md
index 887ae32a6..4ac0e6770 100644
--- a/docs/blog/posts/intel-gaudi.md
+++ b/docs/blog/posts/intel-gaudi.md
@@ -92,10 +92,10 @@ Provisioning...
With your fleet provisioned, you can now run [dev environments](../../docs/concepts/dev-environments.md), [tasks](../../docs/concepts/tasks.md), [services](../../docs/concepts/services.md).
-Below is an example of a task configuration for fine-tuning the [`DeepSeek-R1-Distill-Qwen-7B` :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://huggingface.co/deepseek-ai/DeepSeek-R1-Distill-Qwen-7B){:target="_blank"}
-model using [Optimum for Intel Gaudi :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://github.com/huggingface/optimum-habana){:target="_blank"}
-and [DeepSpeed :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://docs.habana.ai/en/latest/PyTorch/DeepSpeed/DeepSpeed_User_Guide/DeepSpeed_User_Guide.html#deepspeed-user-guide){:target="_blank"} with
-the [`lvwerra/stack-exchange-paired` :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://huggingface.co/datasets/lvwerra/stack-exchange-paired){:target="_blank"} dataset:
+Below is an example of a task configuration for fine-tuning the [`DeepSeek-R1-Distill-Qwen-7B`](https://huggingface.co/deepseek-ai/DeepSeek-R1-Distill-Qwen-7B)
+model using [Optimum for Intel Gaudi](https://github.com/huggingface/optimum-habana)
+and [DeepSpeed](https://docs.habana.ai/en/latest/PyTorch/DeepSpeed/DeepSpeed_User_Guide/DeepSpeed_User_Guide.html#deepspeed-user-guide) with
+the [`lvwerra/stack-exchange-paired`](https://huggingface.co/datasets/lvwerra/stack-exchange-paired) dataset:
@@ -163,7 +163,7 @@ $ dstack apply -f examples/single-node-training/trl/intel/.dstack.yml -R
!!! info "Intel Tiber AI Cloud"
At `dstack`, we’re grateful to be part of the Intel Liftoff program, which allowed us to access Intel Gaudi AI
- accelerators via [Intel Tiber AI Cloud :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://www.intel.com/content/www/us/en/developer/tools/tiber/ai-cloud.html){:target="_blank"}.
+ accelerators via [Intel Tiber AI Cloud](https://www.intel.com/content/www/us/en/developer/tools/tiber/ai-cloud.html).
You can sign up if you’d like to access Intel Gaudi AI accelerators via the cloud.
Native integration with Intel Tiber AI Cloud is also coming soon to `dstack`.
@@ -171,4 +171,4 @@ $ dstack apply -f examples/single-node-training/trl/intel/.dstack.yml -R
!!! info "What's next?"
1. Refer to [Quickstart](../../docs/quickstart.md)
2. Check [dev environments](../../docs/concepts/dev-environments.md), [tasks](../../docs/concepts/tasks.md), [services](../../docs/concepts/services.md), and [fleets](../../docs/concepts/fleets.md)
- 3. Join [Discord :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://discord.gg/u8SmfwPpMd){:target="_blank"}
+ 3. Join [Discord](https://discord.gg/u8SmfwPpMd)
diff --git a/docs/blog/posts/kubernetes-beta.md b/docs/blog/posts/kubernetes-beta.md
index cc2529e7f..6dfc7cd5b 100644
--- a/docs/blog/posts/kubernetes-beta.md
+++ b/docs/blog/posts/kubernetes-beta.md
@@ -29,11 +29,11 @@ A major advantage of Kubernetes is its portability. Whether you’re using manag
!!! info "NVIDIA GPU Operator"
For `dstack` to correctly detect GPUs in your Kubernetes cluster, the cluster must have the
- [NVIDIA GPU Operator :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://docs.nvidia.com/datacenter/cloud-native/gpu-operator/latest/index.html){:target="_blank"} pre-installed.
+ [NVIDIA GPU Operator](https://docs.nvidia.com/datacenter/cloud-native/gpu-operator/latest/index.html) pre-installed.
### Nebius example
-If you're using [Nebius :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://nebius.com/){:target="_blank"}, the process of creating a Kubernetes cluster is straightforward.
+If you're using [Nebius](https://nebius.com/), the process of creating a Kubernetes cluster is straightforward.
Select the region of interest and click `Create cluster`.
Once the cluster is created, switch to `Applications` and install the `nvidia-device-plugin` application — this can be done in one click.
@@ -312,4 +312,4 @@ Support for AMD GPUs is coming soon — our team is actively working on it right
[tasks](../../docs/concepts/tasks.md), [services](../../docs/concepts/services.md),
and [fleets](../../docs/concepts/fleets.md)
3. Read the the [clusters](../../docs/guides/clusters.md) guide
- 4. Join [Discord :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://discord.gg/u8SmfwPpMd){:target="_blank"}
+ 4. Join [Discord](https://discord.gg/u8SmfwPpMd)
diff --git a/docs/blog/posts/metrics-ui.md b/docs/blog/posts/metrics-ui.md
index b15bbffc5..db21cf019 100644
--- a/docs/blog/posts/metrics-ui.md
+++ b/docs/blog/posts/metrics-ui.md
@@ -55,4 +55,4 @@ metrics from `dstack`.
!!! info "What's next?"
1. See [Metrics](../../docs/guides/metrics.md)
2. Check [dev environments](../../docs/concepts/dev-environments.md), [tasks](../../docs/concepts/tasks.md), [services](../../docs/concepts/services.md), and [fleets](../../docs/concepts/fleets.md)
- 3. Join [Discord :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://discord.gg/u8SmfwPpMd){:target="_blank"}
+ 3. Join [Discord](https://discord.gg/u8SmfwPpMd)
diff --git a/docs/blog/posts/mpi.md b/docs/blog/posts/mpi.md
index 5473d64a2..7b4b3d64b 100644
--- a/docs/blog/posts/mpi.md
+++ b/docs/blog/posts/mpi.md
@@ -94,11 +94,11 @@ With this, now you can use such a task to run both NCCL or RCCL tests on both cl
as well as use MPI for other tasks.
> The `dstackai/efa` image used in the example comes with MPI and NCCL tests pre-installed. While it is optimized for
-> [AWS EFA :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://aws.amazon.com/hpc/efa/){:target="_blank"}, it can also
+> [AWS EFA](https://aws.amazon.com/hpc/efa/), it can also
> be used with regular TCP/IP network adapters and InfiniBand.
-> See the [source code :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://github.com/dstackai/dstack/blob/master/docker/efa) for the image.
+> See the [source code](https://github.com/dstackai/dstack/blob/master/docker/efa) for the image.
!!! info "What's next?"
1. Learn more about [dev environments](../../docs/concepts/dev-environments.md), [tasks](../../docs/concepts/tasks.md), [services](../../docs/concepts/services.md), and [fleets](../../docs/concepts/fleets.md)
2. Check the [NCCL tests](../../examples/clusters/nccl-tests/index.md) example
- 3. Join [Discord :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://discord.gg/u8SmfwPpMd){:target="_blank"}
+ 3. Join [Discord](https://discord.gg/u8SmfwPpMd)
diff --git a/docs/blog/posts/nebius-in-dstack-sky.md b/docs/blog/posts/nebius-in-dstack-sky.md
index e05bc2764..a65a06dcf 100644
--- a/docs/blog/posts/nebius-in-dstack-sky.md
+++ b/docs/blog/posts/nebius-in-dstack-sky.md
@@ -8,11 +8,11 @@ categories:
- Changelog
---
-# Nebius joins dstack Sky GPU marketplace, with production-ready GPU clusters
+# Nebius in dstack Sky GPU marketplace, with production-ready GPU clusters
-`dstack` is an [open-source :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://github.com/dstackai/dstack){:target="_blank"} control plane for orchestrating GPU workloads. It can provision cloud VMs, run on top of Kubernetes, or manage on-prem clusters. If you don’t want to self-host, you can use [dstack Sky :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://sky.dstack.ai){:target="_blank"}, the managed version of `dstack` that also provides access to cloud GPUs via its markfetplace.
+`dstack` is an [open-source](https://github.com/dstackai/dstack) control plane for orchestrating GPU workloads. It can provision cloud VMs, run on top of Kubernetes, or manage on-prem clusters. If you don’t want to self-host, you can use [dstack Sky](https://sky.dstack.ai), the managed version of `dstack` that also provides access to cloud GPUs via its markfetplace.
-With our latest release, we’re excited to announce that [Nebius :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://nebius.com/){:target="_blank"}, a purpose-built AI cloud for large scale training and inference, has joined the `dstack` Sky marketplace
+With our latest release, we’re excited to announce that [Nebius](https://nebius.com/), a purpose-built AI cloud for large scale training and inference, has joined the `dstack` Sky marketplace
to offer on-demand and spot GPUs, including clusters.
 @@ -26,7 +26,7 @@ Since early this year, the open-source `dstack` has supported Nebius, making it
## About dstack Sky
-With this week's release, Nebius officially joins [dstack Sky :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://sky.dstack.ai){:target="_blank"}. Nebius can now be used not only with your own account, but also directly via the GPU marketplace.
+With this week's release, Nebius officially joins [dstack Sky](https://sky.dstack.ai). Nebius can now be used not only with your own account, but also directly via the GPU marketplace.
The marketplace lets you access Nebius GPUs without having a Nebius account. You can pay through `dstack Sky`, and switch to your own Nebius account anytime with just a few clicks.
@@ -39,7 +39,7 @@ With Nebius, `dstack` Sky users can orchestrate NVIDIA GPUs provisioned in hours
## Getting started
-After you [sign up :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://sky.dstack.ai){:target="_blank"} with `dstack` Sky,
+After you [sign up](https://sky.dstack.ai) with `dstack` Sky,
you’ll be prompted to create a project and choose between the GPU marketplace or your own cloud account:
@@ -26,7 +26,7 @@ Since early this year, the open-source `dstack` has supported Nebius, making it
## About dstack Sky
-With this week's release, Nebius officially joins [dstack Sky :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://sky.dstack.ai){:target="_blank"}. Nebius can now be used not only with your own account, but also directly via the GPU marketplace.
+With this week's release, Nebius officially joins [dstack Sky](https://sky.dstack.ai). Nebius can now be used not only with your own account, but also directly via the GPU marketplace.
The marketplace lets you access Nebius GPUs without having a Nebius account. You can pay through `dstack Sky`, and switch to your own Nebius account anytime with just a few clicks.
@@ -39,7 +39,7 @@ With Nebius, `dstack` Sky users can orchestrate NVIDIA GPUs provisioned in hours
## Getting started
-After you [sign up :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://sky.dstack.ai){:target="_blank"} with `dstack` Sky,
+After you [sign up](https://sky.dstack.ai) with `dstack` Sky,
you’ll be prompted to create a project and choose between the GPU marketplace or your own cloud account:
 @@ -118,9 +118,9 @@ Our goal is to give teams maximum flexibility while removing the complexity of m
providing a simple, multi-cloud interface for development, training, and inference.
!!! info "What's next"
- 1. Sign up with [dstack Sky :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://sky.dstack.ai){:target="_blank"}
+ 1. Sign up with [dstack Sky](https://sky.dstack.ai)
2. Check [Quickstart](../../docs/quickstart.md)
- 3. Learn more about [Nebius :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://nebius.com/){:target="_blank"}
+ 3. Learn more about [Nebius](https://nebius.com/)
4. Explore [dev environments](../../docs/concepts/dev-environments.md),
[tasks](../../docs/concepts/tasks.md), [services](../../docs/concepts/services.md),
and [fleets](../../docs/concepts/fleets.md)
diff --git a/docs/blog/posts/nebius.md b/docs/blog/posts/nebius.md
index d24681959..c7a280971 100644
--- a/docs/blog/posts/nebius.md
+++ b/docs/blog/posts/nebius.md
@@ -17,7 +17,7 @@ alternative to Kubernetes and Slurm.
@@ -118,9 +118,9 @@ Our goal is to give teams maximum flexibility while removing the complexity of m
providing a simple, multi-cloud interface for development, training, and inference.
!!! info "What's next"
- 1. Sign up with [dstack Sky :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://sky.dstack.ai){:target="_blank"}
+ 1. Sign up with [dstack Sky](https://sky.dstack.ai)
2. Check [Quickstart](../../docs/quickstart.md)
- 3. Learn more about [Nebius :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://nebius.com/){:target="_blank"}
+ 3. Learn more about [Nebius](https://nebius.com/)
4. Explore [dev environments](../../docs/concepts/dev-environments.md),
[tasks](../../docs/concepts/tasks.md), [services](../../docs/concepts/services.md),
and [fleets](../../docs/concepts/fleets.md)
diff --git a/docs/blog/posts/nebius.md b/docs/blog/posts/nebius.md
index d24681959..c7a280971 100644
--- a/docs/blog/posts/nebius.md
+++ b/docs/blog/posts/nebius.md
@@ -17,7 +17,7 @@ alternative to Kubernetes and Slurm.
 -Today, we’re announcing native integration with [Nebius :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://nebius.com/){:target="_blank"},
+Today, we’re announcing native integration with [Nebius](https://nebius.com/),
offering a streamlined developer experience for teams using GPUs for AI workloads.
@@ -44,7 +44,7 @@ long-running services—without the operational overhead.
To use `dstack` with Nebius, configure your `nebius` backend:
-1. Log in to your [Nebius AI Cloud :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://console.eu.nebius.com/){:target="_blank"} account.
+1. Log in to your [Nebius AI Cloud](https://console.eu.nebius.com/) account.
2. Navigate to `Access`, and select `Service Accounts`.
3. Create a new service account, assign it to the `editors` group, and upload an authorized key.
@@ -108,8 +108,8 @@ interconnects is coming soon.
!!! info "What's next?"
1. Check [Quickstart](../../docs/quickstart.md)
- 2. Sign up with [Nebius AI Cloud :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://console.eu.nebius.com/){:target="_blank"}
+ 2. Sign up with [Nebius AI Cloud](https://console.eu.nebius.com/)
3. Read about [dev environments](../../docs/concepts/dev-environments.md),
[tasks](../../docs/concepts/tasks.md), [services](../../docs/concepts/services.md),
and [fleets](../../docs/concepts/fleets.md)
- 4. Join [Discord :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://discord.gg/u8SmfwPpMd){:target="_blank"}
+ 4. Join [Discord](https://discord.gg/u8SmfwPpMd)
diff --git a/docs/blog/posts/nvidia-and-amd-on-vultr.md b/docs/blog/posts/nvidia-and-amd-on-vultr.md
index 2fb30ebbc..ed75607d4 100644
--- a/docs/blog/posts/nvidia-and-amd-on-vultr.md
+++ b/docs/blog/posts/nvidia-and-amd-on-vultr.md
@@ -15,7 +15,7 @@ increasingly important.
At `dstack`, we’re committed to redefining AI container orchestration by prioritizing an AI-native, open-source-first
approach.
Today, we’re excited to share a new integration and partnership
-with [Vultr :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://www.vultr.com/){:target="_blank"}.
+with [Vultr](https://www.vultr.com/).
-Today, we’re announcing native integration with [Nebius :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://nebius.com/){:target="_blank"},
+Today, we’re announcing native integration with [Nebius](https://nebius.com/),
offering a streamlined developer experience for teams using GPUs for AI workloads.
@@ -44,7 +44,7 @@ long-running services—without the operational overhead.
To use `dstack` with Nebius, configure your `nebius` backend:
-1. Log in to your [Nebius AI Cloud :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://console.eu.nebius.com/){:target="_blank"} account.
+1. Log in to your [Nebius AI Cloud](https://console.eu.nebius.com/) account.
2. Navigate to `Access`, and select `Service Accounts`.
3. Create a new service account, assign it to the `editors` group, and upload an authorized key.
@@ -108,8 +108,8 @@ interconnects is coming soon.
!!! info "What's next?"
1. Check [Quickstart](../../docs/quickstart.md)
- 2. Sign up with [Nebius AI Cloud :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://console.eu.nebius.com/){:target="_blank"}
+ 2. Sign up with [Nebius AI Cloud](https://console.eu.nebius.com/)
3. Read about [dev environments](../../docs/concepts/dev-environments.md),
[tasks](../../docs/concepts/tasks.md), [services](../../docs/concepts/services.md),
and [fleets](../../docs/concepts/fleets.md)
- 4. Join [Discord :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://discord.gg/u8SmfwPpMd){:target="_blank"}
+ 4. Join [Discord](https://discord.gg/u8SmfwPpMd)
diff --git a/docs/blog/posts/nvidia-and-amd-on-vultr.md b/docs/blog/posts/nvidia-and-amd-on-vultr.md
index 2fb30ebbc..ed75607d4 100644
--- a/docs/blog/posts/nvidia-and-amd-on-vultr.md
+++ b/docs/blog/posts/nvidia-and-amd-on-vultr.md
@@ -15,7 +15,7 @@ increasingly important.
At `dstack`, we’re committed to redefining AI container orchestration by prioritizing an AI-native, open-source-first
approach.
Today, we’re excited to share a new integration and partnership
-with [Vultr :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://www.vultr.com/){:target="_blank"}.
+with [Vultr](https://www.vultr.com/).
 @@ -26,9 +26,9 @@ and NVIDIA GPUs with greater flexibility and efficiency–using `dstack`.
## About Vultr
-[Vultr :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://www.vultr.com/){:target="_blank"} provides cloud GPUs across 32 regions, supporting both NVIDIA and AMD hardware with on-demand and reserved
+[Vultr](https://www.vultr.com/) provides cloud GPUs across 32 regions, supporting both NVIDIA and AMD hardware with on-demand and reserved
capacity. Their offerings include AMD MI300X and NVIDIA GH200, H200, H100, A100, L40S, and A40, all available at
-competitive [pricing :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://www.vultr.com/pricing/#cloud-gpu){:target="_blank"}.
+competitive [pricing](https://www.vultr.com/pricing/#cloud-gpu).
## Why dstack
@@ -47,7 +47,7 @@ and volumes—so you can focus on building instead of troubleshooting infrastruc
To use `dstack` with your Vultr account, you need to [configure a `vultr` backend](../../docs/concepts/backends.md):
-Log into your [Vultr :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://www.vultr.com/) account, click `Account` in the sidebar, select `API`, find the `Personal Access Token` panel and click the `Enable API` button. In the `Access Control` panel, allow API requests from all addresses or from the subnet where your `dstack` server is deployed.
+Log into your [Vultr](https://www.vultr.com/) account, click `Account` in the sidebar, select `API`, find the `Personal Access Token` panel and click the `Enable API` button. In the `Access Control` panel, allow API requests from all addresses or from the subnet where your `dstack` server is deployed.
Then, go ahead and configure the backend:
@@ -71,8 +71,8 @@ For more details, refer to [Installation](../../docs/installation/index.md).
!!! info "What's next?"
1. Refer to [Quickstart](../../docs/quickstart.md)
- 2. Sign up with [Vultr :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://www.vultr.com/)
+ 2. Sign up with [Vultr](https://www.vultr.com/)
3. Check [dev environments](../../docs/concepts/dev-environments.md),
[tasks](../../docs/concepts/tasks.md), [services](../../docs/concepts/services.md),
and [fleets](../../docs/concepts/fleets.md)
- 4. Join [Discord :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://discord.gg/u8SmfwPpMd){:target="_blank"}
+ 4. Join [Discord](https://discord.gg/u8SmfwPpMd)
diff --git a/docs/blog/posts/nvidia-dgx-spark.md b/docs/blog/posts/nvidia-dgx-spark.md
index a51fee474..60202c60c 100644
--- a/docs/blog/posts/nvidia-dgx-spark.md
+++ b/docs/blog/posts/nvidia-dgx-spark.md
@@ -10,7 +10,7 @@ image: https://dstack.ai/static-assets/static-assets/images/nvidia-dgx-spark.png
# Orchestrating workloads on NVIDIA DGX Spark
-With support from [Graphsignal :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://x.com/GraphsignalAI/status/1986565583593197885){:target="_blank" }, our team gained access to the new [NVIDIA DGX Spark :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://www.nvidia.com/en-us/products/workstations/dgx-spark/){:target="_blank"} and used it to validate how `dstack` operates on this hardware. This post walks through how to set it up with `dstack` and use it alongside existing on-prem clusters or GPU cloud environments to run workloads.
+With support from [Graphsignal](https://x.com/GraphsignalAI/status/1986565583593197885), our team gained access to the new [NVIDIA DGX Spark](https://www.nvidia.com/en-us/products/workstations/dgx-spark/) and used it to validate how `dstack` operates on this hardware. This post walks through how to set it up with `dstack` and use it alongside existing on-prem clusters or GPU cloud environments to run workloads.
@@ -26,9 +26,9 @@ and NVIDIA GPUs with greater flexibility and efficiency–using `dstack`.
## About Vultr
-[Vultr :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://www.vultr.com/){:target="_blank"} provides cloud GPUs across 32 regions, supporting both NVIDIA and AMD hardware with on-demand and reserved
+[Vultr](https://www.vultr.com/) provides cloud GPUs across 32 regions, supporting both NVIDIA and AMD hardware with on-demand and reserved
capacity. Their offerings include AMD MI300X and NVIDIA GH200, H200, H100, A100, L40S, and A40, all available at
-competitive [pricing :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://www.vultr.com/pricing/#cloud-gpu){:target="_blank"}.
+competitive [pricing](https://www.vultr.com/pricing/#cloud-gpu).
## Why dstack
@@ -47,7 +47,7 @@ and volumes—so you can focus on building instead of troubleshooting infrastruc
To use `dstack` with your Vultr account, you need to [configure a `vultr` backend](../../docs/concepts/backends.md):
-Log into your [Vultr :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://www.vultr.com/) account, click `Account` in the sidebar, select `API`, find the `Personal Access Token` panel and click the `Enable API` button. In the `Access Control` panel, allow API requests from all addresses or from the subnet where your `dstack` server is deployed.
+Log into your [Vultr](https://www.vultr.com/) account, click `Account` in the sidebar, select `API`, find the `Personal Access Token` panel and click the `Enable API` button. In the `Access Control` panel, allow API requests from all addresses or from the subnet where your `dstack` server is deployed.
Then, go ahead and configure the backend:
@@ -71,8 +71,8 @@ For more details, refer to [Installation](../../docs/installation/index.md).
!!! info "What's next?"
1. Refer to [Quickstart](../../docs/quickstart.md)
- 2. Sign up with [Vultr :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://www.vultr.com/)
+ 2. Sign up with [Vultr](https://www.vultr.com/)
3. Check [dev environments](../../docs/concepts/dev-environments.md),
[tasks](../../docs/concepts/tasks.md), [services](../../docs/concepts/services.md),
and [fleets](../../docs/concepts/fleets.md)
- 4. Join [Discord :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://discord.gg/u8SmfwPpMd){:target="_blank"}
+ 4. Join [Discord](https://discord.gg/u8SmfwPpMd)
diff --git a/docs/blog/posts/nvidia-dgx-spark.md b/docs/blog/posts/nvidia-dgx-spark.md
index a51fee474..60202c60c 100644
--- a/docs/blog/posts/nvidia-dgx-spark.md
+++ b/docs/blog/posts/nvidia-dgx-spark.md
@@ -10,7 +10,7 @@ image: https://dstack.ai/static-assets/static-assets/images/nvidia-dgx-spark.png
# Orchestrating workloads on NVIDIA DGX Spark
-With support from [Graphsignal :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://x.com/GraphsignalAI/status/1986565583593197885){:target="_blank" }, our team gained access to the new [NVIDIA DGX Spark :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://www.nvidia.com/en-us/products/workstations/dgx-spark/){:target="_blank"} and used it to validate how `dstack` operates on this hardware. This post walks through how to set it up with `dstack` and use it alongside existing on-prem clusters or GPU cloud environments to run workloads.
+With support from [Graphsignal](https://x.com/GraphsignalAI/status/1986565583593197885), our team gained access to the new [NVIDIA DGX Spark](https://www.nvidia.com/en-us/products/workstations/dgx-spark/) and used it to validate how `dstack` operates on this hardware. This post walks through how to set it up with `dstack` and use it alongside existing on-prem clusters or GPU cloud environments to run workloads.
 @@ -121,12 +121,12 @@ To open in VS Code Desktop, use this link:
> Running workloads on DGX Spark with `dstack` works the same way as on any other [backend](../../docs/concepts/backends.md) (including GPU clouds): you can run [dev environments](../../docs/concepts/dev-environments.md) for interactive development, [tasks](../../docs/concepts/tasks.md) for fine tuning, and [services](../../docs/concepts/services.md) for inference through the unified interface.
-1. Read the [NVIDIA DGX Spark in-depth review :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://lmsys.org/blog/2025-10-13-nvidia-dgx-spark/){:target="_blank"} by the SGLang team.
+1. Read the [NVIDIA DGX Spark in-depth review](https://lmsys.org/blog/2025-10-13-nvidia-dgx-spark/) by the SGLang team.
2. Check [dev environments](../../docs/concepts/dev-environments.md),
[tasks](../../docs/concepts/tasks.md), [services](../../docs/concepts/services.md),
and [fleets](../../docs/concepts/fleets.md)
3. Follow [Quickstart](../../docs/quickstart.md)
-4. Join [Discord :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://discord.gg/u8SmfwPpMd){:target="_blank"}
+4. Join [Discord](https://discord.gg/u8SmfwPpMd)
!!! info "Aknowledgement"
- Thanks to the [Graphsignal :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://graphsignal.com/){:target="_blank"} team for access to DGX Spark and for supporting testing and validation. Graphsignal provides inference observability tooling used to profile CUDA workloads during both training and inference.
+ Thanks to the [Graphsignal](https://graphsignal.com/) team for access to DGX Spark and for supporting testing and validation. Graphsignal provides inference observability tooling used to profile CUDA workloads during both training and inference.
diff --git a/docs/blog/posts/probes.md b/docs/blog/posts/probes.md
index 428d0a7fa..d3d85335a 100644
--- a/docs/blog/posts/probes.md
+++ b/docs/blog/posts/probes.md
@@ -108,4 +108,4 @@ See [services](../../docs/concepts/services.md#probes) and the [reference](../..
!!! info "What's next?"
1. Check [Quickstart](../../docs/quickstart.md)
2. Learn about [services](../../docs/concepts/services.md)
- 3. Join [Discord :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://discord.gg/u8SmfwPpMd){:target="_blank"}
+ 3. Join [Discord](https://discord.gg/u8SmfwPpMd)
diff --git a/docs/blog/posts/prometheus.md b/docs/blog/posts/prometheus.md
index 2594619c0..8a4d579c0 100644
--- a/docs/blog/posts/prometheus.md
+++ b/docs/blog/posts/prometheus.md
@@ -63,4 +63,4 @@ For a full list of available metrics and labels, check out [Metrics](../../docs/
1. Check [dev environments](../../docs/concepts/dev-environments.md),
[tasks](../../docs/concepts/tasks.md), [services](../../docs/concepts/services.md),
and [fleets](../../docs/concepts/fleets.md)
- 2. Join [Discord :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://discord.gg/u8SmfwPpMd){:target="_blank"}
+ 2. Join [Discord](https://discord.gg/u8SmfwPpMd)
diff --git a/docs/blog/posts/state-of-cloud-gpu-2025.md b/docs/blog/posts/state-of-cloud-gpu-2025.md
index c689c9c4b..238926ebf 100644
--- a/docs/blog/posts/state-of-cloud-gpu-2025.md
+++ b/docs/blog/posts/state-of-cloud-gpu-2025.md
@@ -135,11 +135,11 @@ This turns capacity from individual silos into one fungible pool.
- **Next steps.** We plan to publish price normalization, hardware/network microbenchmarks, and a scheduler capability matrix; preliminary harnesses are linked in the appendix. Contributors welcome.
-> If you need a lighter, simpler orchestration and control-plane alternative to Kubernetes or Slurm, consider [dstack :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://github.com/dstackai/dstack/){:target="_blank"}.
+> If you need a lighter, simpler orchestration and control-plane alternative to Kubernetes or Slurm, consider [dstack](https://github.com/dstackai/dstack/).
It’s open-source and self-hosted.
??? info "dstack Sky"
- If you want unified access to low-cost on-demand and spot GPUs across multiple clouds, try [dstack Sky :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://sky.dstack.ai/){:target="_blank"}.
+ If you want unified access to low-cost on-demand and spot GPUs across multiple clouds, try [dstack Sky](https://sky.dstack.ai/).
@@ -121,12 +121,12 @@ To open in VS Code Desktop, use this link:
> Running workloads on DGX Spark with `dstack` works the same way as on any other [backend](../../docs/concepts/backends.md) (including GPU clouds): you can run [dev environments](../../docs/concepts/dev-environments.md) for interactive development, [tasks](../../docs/concepts/tasks.md) for fine tuning, and [services](../../docs/concepts/services.md) for inference through the unified interface.
-1. Read the [NVIDIA DGX Spark in-depth review :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://lmsys.org/blog/2025-10-13-nvidia-dgx-spark/){:target="_blank"} by the SGLang team.
+1. Read the [NVIDIA DGX Spark in-depth review](https://lmsys.org/blog/2025-10-13-nvidia-dgx-spark/) by the SGLang team.
2. Check [dev environments](../../docs/concepts/dev-environments.md),
[tasks](../../docs/concepts/tasks.md), [services](../../docs/concepts/services.md),
and [fleets](../../docs/concepts/fleets.md)
3. Follow [Quickstart](../../docs/quickstart.md)
-4. Join [Discord :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://discord.gg/u8SmfwPpMd){:target="_blank"}
+4. Join [Discord](https://discord.gg/u8SmfwPpMd)
!!! info "Aknowledgement"
- Thanks to the [Graphsignal :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://graphsignal.com/){:target="_blank"} team for access to DGX Spark and for supporting testing and validation. Graphsignal provides inference observability tooling used to profile CUDA workloads during both training and inference.
+ Thanks to the [Graphsignal](https://graphsignal.com/) team for access to DGX Spark and for supporting testing and validation. Graphsignal provides inference observability tooling used to profile CUDA workloads during both training and inference.
diff --git a/docs/blog/posts/probes.md b/docs/blog/posts/probes.md
index 428d0a7fa..d3d85335a 100644
--- a/docs/blog/posts/probes.md
+++ b/docs/blog/posts/probes.md
@@ -108,4 +108,4 @@ See [services](../../docs/concepts/services.md#probes) and the [reference](../..
!!! info "What's next?"
1. Check [Quickstart](../../docs/quickstart.md)
2. Learn about [services](../../docs/concepts/services.md)
- 3. Join [Discord :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://discord.gg/u8SmfwPpMd){:target="_blank"}
+ 3. Join [Discord](https://discord.gg/u8SmfwPpMd)
diff --git a/docs/blog/posts/prometheus.md b/docs/blog/posts/prometheus.md
index 2594619c0..8a4d579c0 100644
--- a/docs/blog/posts/prometheus.md
+++ b/docs/blog/posts/prometheus.md
@@ -63,4 +63,4 @@ For a full list of available metrics and labels, check out [Metrics](../../docs/
1. Check [dev environments](../../docs/concepts/dev-environments.md),
[tasks](../../docs/concepts/tasks.md), [services](../../docs/concepts/services.md),
and [fleets](../../docs/concepts/fleets.md)
- 2. Join [Discord :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://discord.gg/u8SmfwPpMd){:target="_blank"}
+ 2. Join [Discord](https://discord.gg/u8SmfwPpMd)
diff --git a/docs/blog/posts/state-of-cloud-gpu-2025.md b/docs/blog/posts/state-of-cloud-gpu-2025.md
index c689c9c4b..238926ebf 100644
--- a/docs/blog/posts/state-of-cloud-gpu-2025.md
+++ b/docs/blog/posts/state-of-cloud-gpu-2025.md
@@ -135,11 +135,11 @@ This turns capacity from individual silos into one fungible pool.
- **Next steps.** We plan to publish price normalization, hardware/network microbenchmarks, and a scheduler capability matrix; preliminary harnesses are linked in the appendix. Contributors welcome.
-> If you need a lighter, simpler orchestration and control-plane alternative to Kubernetes or Slurm, consider [dstack :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://github.com/dstackai/dstack/){:target="_blank"}.
+> If you need a lighter, simpler orchestration and control-plane alternative to Kubernetes or Slurm, consider [dstack](https://github.com/dstackai/dstack/).
It’s open-source and self-hosted.
??? info "dstack Sky"
- If you want unified access to low-cost on-demand and spot GPUs across multiple clouds, try [dstack Sky :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://sky.dstack.ai/){:target="_blank"}.
+ If you want unified access to low-cost on-demand and spot GPUs across multiple clouds, try [dstack Sky](https://sky.dstack.ai/).
 diff --git a/docs/blog/posts/tpu-on-gcp.md b/docs/blog/posts/tpu-on-gcp.md
index 8fff83cb4..4a45af000 100644
--- a/docs/blog/posts/tpu-on-gcp.md
+++ b/docs/blog/posts/tpu-on-gcp.md
@@ -14,8 +14,8 @@ If you’re using or planning to use TPUs with Google Cloud, you can now do so v
Read below to find out how to use TPUs with `dstack` for fine-tuning and deploying
LLMs, leveraging open-source tools like Hugging Face’s
-[Optimum TPU :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://github.com/huggingface/optimum-tpu){:target="_blank"}
-and [vLLM :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://docs.vllm.ai/en/latest/getting_started/tpu-installation.html){:target="_blank"}.
+[Optimum TPU](https://github.com/huggingface/optimum-tpu)
+and [vLLM](https://docs.vllm.ai/en/latest/getting_started/tpu-installation.html).
@@ -45,8 +45,8 @@ If you've configured the `gcp` backend, `dstack` will automatically provision th
You can use any serving framework, such as vLLM, TGI. Here's an example of a [service](https://dstack.ai/docs/services) that deploys
Llama 3.1 8B using
-[Optimum TPU :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://github.com/huggingface/optimum-tpu){:target="_blank"}
-and [vLLM :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://github.com/vllm-project/vllm){:target="_blank"}.
+[Optimum TPU](https://github.com/huggingface/optimum-tpu)
+and [vLLM](https://github.com/vllm-project/vllm).
=== "Optimum TPU"
@@ -79,7 +79,7 @@ and [vLLM :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://github.com/vllm-
```
diff --git a/docs/blog/posts/tpu-on-gcp.md b/docs/blog/posts/tpu-on-gcp.md
index 8fff83cb4..4a45af000 100644
--- a/docs/blog/posts/tpu-on-gcp.md
+++ b/docs/blog/posts/tpu-on-gcp.md
@@ -14,8 +14,8 @@ If you’re using or planning to use TPUs with Google Cloud, you can now do so v
Read below to find out how to use TPUs with `dstack` for fine-tuning and deploying
LLMs, leveraging open-source tools like Hugging Face’s
-[Optimum TPU :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://github.com/huggingface/optimum-tpu){:target="_blank"}
-and [vLLM :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://docs.vllm.ai/en/latest/getting_started/tpu-installation.html){:target="_blank"}.
+[Optimum TPU](https://github.com/huggingface/optimum-tpu)
+and [vLLM](https://docs.vllm.ai/en/latest/getting_started/tpu-installation.html).
@@ -45,8 +45,8 @@ If you've configured the `gcp` backend, `dstack` will automatically provision th
You can use any serving framework, such as vLLM, TGI. Here's an example of a [service](https://dstack.ai/docs/services) that deploys
Llama 3.1 8B using
-[Optimum TPU :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://github.com/huggingface/optimum-tpu){:target="_blank"}
-and [vLLM :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://github.com/vllm-project/vllm){:target="_blank"}.
+[Optimum TPU](https://github.com/huggingface/optimum-tpu)
+and [vLLM](https://github.com/vllm-project/vllm).
=== "Optimum TPU"
@@ -79,7 +79,7 @@ and [vLLM :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://github.com/vllm-
```
- Once the [pull request :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://github.com/huggingface/optimum-tpu/pull/87){:target="_blank"} is merged,
+ Once the [pull request](https://github.com/huggingface/optimum-tpu/pull/87) is merged,
the official Docker image can be used instead of `dstackai/optimum-tpu:llama31`.
=== "vLLM"
@@ -145,7 +145,7 @@ Note, `v5litepod` is optimized for serving transformer-based models. Each core i
| Framework | Quantization | Note |
|-----------|----------------|--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|
| **TGI** | bfloat16 | To deploy with TGI, Optimum TPU must be used. |
-| **vLLM** | int8, bfloat16 | int8 quantization still requires the same memory because the weights are first moved to the TPU in bfloat16, and then converted to int8. See the [pull request :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://github.com/vllm-project/vllm/pull/7005){:target="_blank"} for more details. |
+| **vLLM** | int8, bfloat16 | int8 quantization still requires the same memory because the weights are first moved to the TPU in bfloat16, and then converted to int8. See the [pull request](https://github.com/vllm-project/vllm/pull/7005) for more details. |
### Running a configuration
@@ -154,8 +154,8 @@ cloud resources and run the configuration.
## Fine-tuning
-Below is an example of fine-tuning Llama 3.1 8B using [Optimum TPU :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://github.com/huggingface/optimum-tpu){:target="_blank"}
-and the [Abirate/english_quotes :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://huggingface.co/datasets/Abirate/english_quotes){:target="_blank"}
+Below is an example of fine-tuning Llama 3.1 8B using [Optimum TPU](https://github.com/huggingface/optimum-tpu)
+and the [Abirate/english_quotes](https://huggingface.co/datasets/Abirate/english_quotes)
dataset.
 @@ -26,7 +26,7 @@ Since early this year, the open-source `dstack` has supported Nebius, making it
## About dstack Sky
-With this week's release, Nebius officially joins [dstack Sky :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://sky.dstack.ai){:target="_blank"}. Nebius can now be used not only with your own account, but also directly via the GPU marketplace.
+With this week's release, Nebius officially joins [dstack Sky](https://sky.dstack.ai). Nebius can now be used not only with your own account, but also directly via the GPU marketplace.
The marketplace lets you access Nebius GPUs without having a Nebius account. You can pay through `dstack Sky`, and switch to your own Nebius account anytime with just a few clicks.
@@ -39,7 +39,7 @@ With Nebius, `dstack` Sky users can orchestrate NVIDIA GPUs provisioned in hours
## Getting started
-After you [sign up :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://sky.dstack.ai){:target="_blank"} with `dstack` Sky,
+After you [sign up](https://sky.dstack.ai) with `dstack` Sky,
you’ll be prompted to create a project and choose between the GPU marketplace or your own cloud account:
@@ -26,7 +26,7 @@ Since early this year, the open-source `dstack` has supported Nebius, making it
## About dstack Sky
-With this week's release, Nebius officially joins [dstack Sky :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://sky.dstack.ai){:target="_blank"}. Nebius can now be used not only with your own account, but also directly via the GPU marketplace.
+With this week's release, Nebius officially joins [dstack Sky](https://sky.dstack.ai). Nebius can now be used not only with your own account, but also directly via the GPU marketplace.
The marketplace lets you access Nebius GPUs without having a Nebius account. You can pay through `dstack Sky`, and switch to your own Nebius account anytime with just a few clicks.
@@ -39,7 +39,7 @@ With Nebius, `dstack` Sky users can orchestrate NVIDIA GPUs provisioned in hours
## Getting started
-After you [sign up :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://sky.dstack.ai){:target="_blank"} with `dstack` Sky,
+After you [sign up](https://sky.dstack.ai) with `dstack` Sky,
you’ll be prompted to create a project and choose between the GPU marketplace or your own cloud account:
 @@ -118,9 +118,9 @@ Our goal is to give teams maximum flexibility while removing the complexity of m
providing a simple, multi-cloud interface for development, training, and inference.
!!! info "What's next"
- 1. Sign up with [dstack Sky :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://sky.dstack.ai){:target="_blank"}
+ 1. Sign up with [dstack Sky](https://sky.dstack.ai)
2. Check [Quickstart](../../docs/quickstart.md)
- 3. Learn more about [Nebius :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://nebius.com/){:target="_blank"}
+ 3. Learn more about [Nebius](https://nebius.com/)
4. Explore [dev environments](../../docs/concepts/dev-environments.md),
[tasks](../../docs/concepts/tasks.md), [services](../../docs/concepts/services.md),
and [fleets](../../docs/concepts/fleets.md)
diff --git a/docs/blog/posts/nebius.md b/docs/blog/posts/nebius.md
index d24681959..c7a280971 100644
--- a/docs/blog/posts/nebius.md
+++ b/docs/blog/posts/nebius.md
@@ -17,7 +17,7 @@ alternative to Kubernetes and Slurm.
@@ -118,9 +118,9 @@ Our goal is to give teams maximum flexibility while removing the complexity of m
providing a simple, multi-cloud interface for development, training, and inference.
!!! info "What's next"
- 1. Sign up with [dstack Sky :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://sky.dstack.ai){:target="_blank"}
+ 1. Sign up with [dstack Sky](https://sky.dstack.ai)
2. Check [Quickstart](../../docs/quickstart.md)
- 3. Learn more about [Nebius :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://nebius.com/){:target="_blank"}
+ 3. Learn more about [Nebius](https://nebius.com/)
4. Explore [dev environments](../../docs/concepts/dev-environments.md),
[tasks](../../docs/concepts/tasks.md), [services](../../docs/concepts/services.md),
and [fleets](../../docs/concepts/fleets.md)
diff --git a/docs/blog/posts/nebius.md b/docs/blog/posts/nebius.md
index d24681959..c7a280971 100644
--- a/docs/blog/posts/nebius.md
+++ b/docs/blog/posts/nebius.md
@@ -17,7 +17,7 @@ alternative to Kubernetes and Slurm.
 -Today, we’re announcing native integration with [Nebius :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://nebius.com/){:target="_blank"},
+Today, we’re announcing native integration with [Nebius](https://nebius.com/),
offering a streamlined developer experience for teams using GPUs for AI workloads.
@@ -44,7 +44,7 @@ long-running services—without the operational overhead.
To use `dstack` with Nebius, configure your `nebius` backend:
-1. Log in to your [Nebius AI Cloud :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://console.eu.nebius.com/){:target="_blank"} account.
+1. Log in to your [Nebius AI Cloud](https://console.eu.nebius.com/) account.
2. Navigate to `Access`, and select `Service Accounts`.
3. Create a new service account, assign it to the `editors` group, and upload an authorized key.
@@ -108,8 +108,8 @@ interconnects is coming soon.
!!! info "What's next?"
1. Check [Quickstart](../../docs/quickstart.md)
- 2. Sign up with [Nebius AI Cloud :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://console.eu.nebius.com/){:target="_blank"}
+ 2. Sign up with [Nebius AI Cloud](https://console.eu.nebius.com/)
3. Read about [dev environments](../../docs/concepts/dev-environments.md),
[tasks](../../docs/concepts/tasks.md), [services](../../docs/concepts/services.md),
and [fleets](../../docs/concepts/fleets.md)
- 4. Join [Discord :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://discord.gg/u8SmfwPpMd){:target="_blank"}
+ 4. Join [Discord](https://discord.gg/u8SmfwPpMd)
diff --git a/docs/blog/posts/nvidia-and-amd-on-vultr.md b/docs/blog/posts/nvidia-and-amd-on-vultr.md
index 2fb30ebbc..ed75607d4 100644
--- a/docs/blog/posts/nvidia-and-amd-on-vultr.md
+++ b/docs/blog/posts/nvidia-and-amd-on-vultr.md
@@ -15,7 +15,7 @@ increasingly important.
At `dstack`, we’re committed to redefining AI container orchestration by prioritizing an AI-native, open-source-first
approach.
Today, we’re excited to share a new integration and partnership
-with [Vultr :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://www.vultr.com/){:target="_blank"}.
+with [Vultr](https://www.vultr.com/).
-Today, we’re announcing native integration with [Nebius :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://nebius.com/){:target="_blank"},
+Today, we’re announcing native integration with [Nebius](https://nebius.com/),
offering a streamlined developer experience for teams using GPUs for AI workloads.
@@ -44,7 +44,7 @@ long-running services—without the operational overhead.
To use `dstack` with Nebius, configure your `nebius` backend:
-1. Log in to your [Nebius AI Cloud :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://console.eu.nebius.com/){:target="_blank"} account.
+1. Log in to your [Nebius AI Cloud](https://console.eu.nebius.com/) account.
2. Navigate to `Access`, and select `Service Accounts`.
3. Create a new service account, assign it to the `editors` group, and upload an authorized key.
@@ -108,8 +108,8 @@ interconnects is coming soon.
!!! info "What's next?"
1. Check [Quickstart](../../docs/quickstart.md)
- 2. Sign up with [Nebius AI Cloud :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://console.eu.nebius.com/){:target="_blank"}
+ 2. Sign up with [Nebius AI Cloud](https://console.eu.nebius.com/)
3. Read about [dev environments](../../docs/concepts/dev-environments.md),
[tasks](../../docs/concepts/tasks.md), [services](../../docs/concepts/services.md),
and [fleets](../../docs/concepts/fleets.md)
- 4. Join [Discord :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://discord.gg/u8SmfwPpMd){:target="_blank"}
+ 4. Join [Discord](https://discord.gg/u8SmfwPpMd)
diff --git a/docs/blog/posts/nvidia-and-amd-on-vultr.md b/docs/blog/posts/nvidia-and-amd-on-vultr.md
index 2fb30ebbc..ed75607d4 100644
--- a/docs/blog/posts/nvidia-and-amd-on-vultr.md
+++ b/docs/blog/posts/nvidia-and-amd-on-vultr.md
@@ -15,7 +15,7 @@ increasingly important.
At `dstack`, we’re committed to redefining AI container orchestration by prioritizing an AI-native, open-source-first
approach.
Today, we’re excited to share a new integration and partnership
-with [Vultr :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://www.vultr.com/){:target="_blank"}.
+with [Vultr](https://www.vultr.com/).
 @@ -26,9 +26,9 @@ and NVIDIA GPUs with greater flexibility and efficiency–using `dstack`.
## About Vultr
-[Vultr :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://www.vultr.com/){:target="_blank"} provides cloud GPUs across 32 regions, supporting both NVIDIA and AMD hardware with on-demand and reserved
+[Vultr](https://www.vultr.com/) provides cloud GPUs across 32 regions, supporting both NVIDIA and AMD hardware with on-demand and reserved
capacity. Their offerings include AMD MI300X and NVIDIA GH200, H200, H100, A100, L40S, and A40, all available at
-competitive [pricing :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://www.vultr.com/pricing/#cloud-gpu){:target="_blank"}.
+competitive [pricing](https://www.vultr.com/pricing/#cloud-gpu).
## Why dstack
@@ -47,7 +47,7 @@ and volumes—so you can focus on building instead of troubleshooting infrastruc
To use `dstack` with your Vultr account, you need to [configure a `vultr` backend](../../docs/concepts/backends.md):
-Log into your [Vultr :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://www.vultr.com/) account, click `Account` in the sidebar, select `API`, find the `Personal Access Token` panel and click the `Enable API` button. In the `Access Control` panel, allow API requests from all addresses or from the subnet where your `dstack` server is deployed.
+Log into your [Vultr](https://www.vultr.com/) account, click `Account` in the sidebar, select `API`, find the `Personal Access Token` panel and click the `Enable API` button. In the `Access Control` panel, allow API requests from all addresses or from the subnet where your `dstack` server is deployed.
Then, go ahead and configure the backend:
@@ -71,8 +71,8 @@ For more details, refer to [Installation](../../docs/installation/index.md).
!!! info "What's next?"
1. Refer to [Quickstart](../../docs/quickstart.md)
- 2. Sign up with [Vultr :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://www.vultr.com/)
+ 2. Sign up with [Vultr](https://www.vultr.com/)
3. Check [dev environments](../../docs/concepts/dev-environments.md),
[tasks](../../docs/concepts/tasks.md), [services](../../docs/concepts/services.md),
and [fleets](../../docs/concepts/fleets.md)
- 4. Join [Discord :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://discord.gg/u8SmfwPpMd){:target="_blank"}
+ 4. Join [Discord](https://discord.gg/u8SmfwPpMd)
diff --git a/docs/blog/posts/nvidia-dgx-spark.md b/docs/blog/posts/nvidia-dgx-spark.md
index a51fee474..60202c60c 100644
--- a/docs/blog/posts/nvidia-dgx-spark.md
+++ b/docs/blog/posts/nvidia-dgx-spark.md
@@ -10,7 +10,7 @@ image: https://dstack.ai/static-assets/static-assets/images/nvidia-dgx-spark.png
# Orchestrating workloads on NVIDIA DGX Spark
-With support from [Graphsignal :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://x.com/GraphsignalAI/status/1986565583593197885){:target="_blank" }, our team gained access to the new [NVIDIA DGX Spark :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://www.nvidia.com/en-us/products/workstations/dgx-spark/){:target="_blank"} and used it to validate how `dstack` operates on this hardware. This post walks through how to set it up with `dstack` and use it alongside existing on-prem clusters or GPU cloud environments to run workloads.
+With support from [Graphsignal](https://x.com/GraphsignalAI/status/1986565583593197885), our team gained access to the new [NVIDIA DGX Spark](https://www.nvidia.com/en-us/products/workstations/dgx-spark/) and used it to validate how `dstack` operates on this hardware. This post walks through how to set it up with `dstack` and use it alongside existing on-prem clusters or GPU cloud environments to run workloads.
@@ -26,9 +26,9 @@ and NVIDIA GPUs with greater flexibility and efficiency–using `dstack`.
## About Vultr
-[Vultr :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://www.vultr.com/){:target="_blank"} provides cloud GPUs across 32 regions, supporting both NVIDIA and AMD hardware with on-demand and reserved
+[Vultr](https://www.vultr.com/) provides cloud GPUs across 32 regions, supporting both NVIDIA and AMD hardware with on-demand and reserved
capacity. Their offerings include AMD MI300X and NVIDIA GH200, H200, H100, A100, L40S, and A40, all available at
-competitive [pricing :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://www.vultr.com/pricing/#cloud-gpu){:target="_blank"}.
+competitive [pricing](https://www.vultr.com/pricing/#cloud-gpu).
## Why dstack
@@ -47,7 +47,7 @@ and volumes—so you can focus on building instead of troubleshooting infrastruc
To use `dstack` with your Vultr account, you need to [configure a `vultr` backend](../../docs/concepts/backends.md):
-Log into your [Vultr :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://www.vultr.com/) account, click `Account` in the sidebar, select `API`, find the `Personal Access Token` panel and click the `Enable API` button. In the `Access Control` panel, allow API requests from all addresses or from the subnet where your `dstack` server is deployed.
+Log into your [Vultr](https://www.vultr.com/) account, click `Account` in the sidebar, select `API`, find the `Personal Access Token` panel and click the `Enable API` button. In the `Access Control` panel, allow API requests from all addresses or from the subnet where your `dstack` server is deployed.
Then, go ahead and configure the backend:
@@ -71,8 +71,8 @@ For more details, refer to [Installation](../../docs/installation/index.md).
!!! info "What's next?"
1. Refer to [Quickstart](../../docs/quickstart.md)
- 2. Sign up with [Vultr :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://www.vultr.com/)
+ 2. Sign up with [Vultr](https://www.vultr.com/)
3. Check [dev environments](../../docs/concepts/dev-environments.md),
[tasks](../../docs/concepts/tasks.md), [services](../../docs/concepts/services.md),
and [fleets](../../docs/concepts/fleets.md)
- 4. Join [Discord :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://discord.gg/u8SmfwPpMd){:target="_blank"}
+ 4. Join [Discord](https://discord.gg/u8SmfwPpMd)
diff --git a/docs/blog/posts/nvidia-dgx-spark.md b/docs/blog/posts/nvidia-dgx-spark.md
index a51fee474..60202c60c 100644
--- a/docs/blog/posts/nvidia-dgx-spark.md
+++ b/docs/blog/posts/nvidia-dgx-spark.md
@@ -10,7 +10,7 @@ image: https://dstack.ai/static-assets/static-assets/images/nvidia-dgx-spark.png
# Orchestrating workloads on NVIDIA DGX Spark
-With support from [Graphsignal :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://x.com/GraphsignalAI/status/1986565583593197885){:target="_blank" }, our team gained access to the new [NVIDIA DGX Spark :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://www.nvidia.com/en-us/products/workstations/dgx-spark/){:target="_blank"} and used it to validate how `dstack` operates on this hardware. This post walks through how to set it up with `dstack` and use it alongside existing on-prem clusters or GPU cloud environments to run workloads.
+With support from [Graphsignal](https://x.com/GraphsignalAI/status/1986565583593197885), our team gained access to the new [NVIDIA DGX Spark](https://www.nvidia.com/en-us/products/workstations/dgx-spark/) and used it to validate how `dstack` operates on this hardware. This post walks through how to set it up with `dstack` and use it alongside existing on-prem clusters or GPU cloud environments to run workloads.
 @@ -121,12 +121,12 @@ To open in VS Code Desktop, use this link:
> Running workloads on DGX Spark with `dstack` works the same way as on any other [backend](../../docs/concepts/backends.md) (including GPU clouds): you can run [dev environments](../../docs/concepts/dev-environments.md) for interactive development, [tasks](../../docs/concepts/tasks.md) for fine tuning, and [services](../../docs/concepts/services.md) for inference through the unified interface.
-1. Read the [NVIDIA DGX Spark in-depth review :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://lmsys.org/blog/2025-10-13-nvidia-dgx-spark/){:target="_blank"} by the SGLang team.
+1. Read the [NVIDIA DGX Spark in-depth review](https://lmsys.org/blog/2025-10-13-nvidia-dgx-spark/) by the SGLang team.
2. Check [dev environments](../../docs/concepts/dev-environments.md),
[tasks](../../docs/concepts/tasks.md), [services](../../docs/concepts/services.md),
and [fleets](../../docs/concepts/fleets.md)
3. Follow [Quickstart](../../docs/quickstart.md)
-4. Join [Discord :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://discord.gg/u8SmfwPpMd){:target="_blank"}
+4. Join [Discord](https://discord.gg/u8SmfwPpMd)
!!! info "Aknowledgement"
- Thanks to the [Graphsignal :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://graphsignal.com/){:target="_blank"} team for access to DGX Spark and for supporting testing and validation. Graphsignal provides inference observability tooling used to profile CUDA workloads during both training and inference.
+ Thanks to the [Graphsignal](https://graphsignal.com/) team for access to DGX Spark and for supporting testing and validation. Graphsignal provides inference observability tooling used to profile CUDA workloads during both training and inference.
diff --git a/docs/blog/posts/probes.md b/docs/blog/posts/probes.md
index 428d0a7fa..d3d85335a 100644
--- a/docs/blog/posts/probes.md
+++ b/docs/blog/posts/probes.md
@@ -108,4 +108,4 @@ See [services](../../docs/concepts/services.md#probes) and the [reference](../..
!!! info "What's next?"
1. Check [Quickstart](../../docs/quickstart.md)
2. Learn about [services](../../docs/concepts/services.md)
- 3. Join [Discord :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://discord.gg/u8SmfwPpMd){:target="_blank"}
+ 3. Join [Discord](https://discord.gg/u8SmfwPpMd)
diff --git a/docs/blog/posts/prometheus.md b/docs/blog/posts/prometheus.md
index 2594619c0..8a4d579c0 100644
--- a/docs/blog/posts/prometheus.md
+++ b/docs/blog/posts/prometheus.md
@@ -63,4 +63,4 @@ For a full list of available metrics and labels, check out [Metrics](../../docs/
1. Check [dev environments](../../docs/concepts/dev-environments.md),
[tasks](../../docs/concepts/tasks.md), [services](../../docs/concepts/services.md),
and [fleets](../../docs/concepts/fleets.md)
- 2. Join [Discord :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://discord.gg/u8SmfwPpMd){:target="_blank"}
+ 2. Join [Discord](https://discord.gg/u8SmfwPpMd)
diff --git a/docs/blog/posts/state-of-cloud-gpu-2025.md b/docs/blog/posts/state-of-cloud-gpu-2025.md
index c689c9c4b..238926ebf 100644
--- a/docs/blog/posts/state-of-cloud-gpu-2025.md
+++ b/docs/blog/posts/state-of-cloud-gpu-2025.md
@@ -135,11 +135,11 @@ This turns capacity from individual silos into one fungible pool.
- **Next steps.** We plan to publish price normalization, hardware/network microbenchmarks, and a scheduler capability matrix; preliminary harnesses are linked in the appendix. Contributors welcome.
-> If you need a lighter, simpler orchestration and control-plane alternative to Kubernetes or Slurm, consider [dstack :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://github.com/dstackai/dstack/){:target="_blank"}.
+> If you need a lighter, simpler orchestration and control-plane alternative to Kubernetes or Slurm, consider [dstack](https://github.com/dstackai/dstack/).
It’s open-source and self-hosted.
??? info "dstack Sky"
- If you want unified access to low-cost on-demand and spot GPUs across multiple clouds, try [dstack Sky :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://sky.dstack.ai/){:target="_blank"}.
+ If you want unified access to low-cost on-demand and spot GPUs across multiple clouds, try [dstack Sky](https://sky.dstack.ai/).
@@ -121,12 +121,12 @@ To open in VS Code Desktop, use this link:
> Running workloads on DGX Spark with `dstack` works the same way as on any other [backend](../../docs/concepts/backends.md) (including GPU clouds): you can run [dev environments](../../docs/concepts/dev-environments.md) for interactive development, [tasks](../../docs/concepts/tasks.md) for fine tuning, and [services](../../docs/concepts/services.md) for inference through the unified interface.
-1. Read the [NVIDIA DGX Spark in-depth review :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://lmsys.org/blog/2025-10-13-nvidia-dgx-spark/){:target="_blank"} by the SGLang team.
+1. Read the [NVIDIA DGX Spark in-depth review](https://lmsys.org/blog/2025-10-13-nvidia-dgx-spark/) by the SGLang team.
2. Check [dev environments](../../docs/concepts/dev-environments.md),
[tasks](../../docs/concepts/tasks.md), [services](../../docs/concepts/services.md),
and [fleets](../../docs/concepts/fleets.md)
3. Follow [Quickstart](../../docs/quickstart.md)
-4. Join [Discord :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://discord.gg/u8SmfwPpMd){:target="_blank"}
+4. Join [Discord](https://discord.gg/u8SmfwPpMd)
!!! info "Aknowledgement"
- Thanks to the [Graphsignal :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://graphsignal.com/){:target="_blank"} team for access to DGX Spark and for supporting testing and validation. Graphsignal provides inference observability tooling used to profile CUDA workloads during both training and inference.
+ Thanks to the [Graphsignal](https://graphsignal.com/) team for access to DGX Spark and for supporting testing and validation. Graphsignal provides inference observability tooling used to profile CUDA workloads during both training and inference.
diff --git a/docs/blog/posts/probes.md b/docs/blog/posts/probes.md
index 428d0a7fa..d3d85335a 100644
--- a/docs/blog/posts/probes.md
+++ b/docs/blog/posts/probes.md
@@ -108,4 +108,4 @@ See [services](../../docs/concepts/services.md#probes) and the [reference](../..
!!! info "What's next?"
1. Check [Quickstart](../../docs/quickstart.md)
2. Learn about [services](../../docs/concepts/services.md)
- 3. Join [Discord :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://discord.gg/u8SmfwPpMd){:target="_blank"}
+ 3. Join [Discord](https://discord.gg/u8SmfwPpMd)
diff --git a/docs/blog/posts/prometheus.md b/docs/blog/posts/prometheus.md
index 2594619c0..8a4d579c0 100644
--- a/docs/blog/posts/prometheus.md
+++ b/docs/blog/posts/prometheus.md
@@ -63,4 +63,4 @@ For a full list of available metrics and labels, check out [Metrics](../../docs/
1. Check [dev environments](../../docs/concepts/dev-environments.md),
[tasks](../../docs/concepts/tasks.md), [services](../../docs/concepts/services.md),
and [fleets](../../docs/concepts/fleets.md)
- 2. Join [Discord :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://discord.gg/u8SmfwPpMd){:target="_blank"}
+ 2. Join [Discord](https://discord.gg/u8SmfwPpMd)
diff --git a/docs/blog/posts/state-of-cloud-gpu-2025.md b/docs/blog/posts/state-of-cloud-gpu-2025.md
index c689c9c4b..238926ebf 100644
--- a/docs/blog/posts/state-of-cloud-gpu-2025.md
+++ b/docs/blog/posts/state-of-cloud-gpu-2025.md
@@ -135,11 +135,11 @@ This turns capacity from individual silos into one fungible pool.
- **Next steps.** We plan to publish price normalization, hardware/network microbenchmarks, and a scheduler capability matrix; preliminary harnesses are linked in the appendix. Contributors welcome.
-> If you need a lighter, simpler orchestration and control-plane alternative to Kubernetes or Slurm, consider [dstack :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://github.com/dstackai/dstack/){:target="_blank"}.
+> If you need a lighter, simpler orchestration and control-plane alternative to Kubernetes or Slurm, consider [dstack](https://github.com/dstackai/dstack/).
It’s open-source and self-hosted.
??? info "dstack Sky"
- If you want unified access to low-cost on-demand and spot GPUs across multiple clouds, try [dstack Sky :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://sky.dstack.ai/){:target="_blank"}.
+ If you want unified access to low-cost on-demand and spot GPUs across multiple clouds, try [dstack Sky](https://sky.dstack.ai/).
 diff --git a/docs/blog/posts/tpu-on-gcp.md b/docs/blog/posts/tpu-on-gcp.md
index 8fff83cb4..4a45af000 100644
--- a/docs/blog/posts/tpu-on-gcp.md
+++ b/docs/blog/posts/tpu-on-gcp.md
@@ -14,8 +14,8 @@ If you’re using or planning to use TPUs with Google Cloud, you can now do so v
Read below to find out how to use TPUs with `dstack` for fine-tuning and deploying
LLMs, leveraging open-source tools like Hugging Face’s
-[Optimum TPU :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://github.com/huggingface/optimum-tpu){:target="_blank"}
-and [vLLM :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://docs.vllm.ai/en/latest/getting_started/tpu-installation.html){:target="_blank"}.
+[Optimum TPU](https://github.com/huggingface/optimum-tpu)
+and [vLLM](https://docs.vllm.ai/en/latest/getting_started/tpu-installation.html).
@@ -45,8 +45,8 @@ If you've configured the `gcp` backend, `dstack` will automatically provision th
You can use any serving framework, such as vLLM, TGI. Here's an example of a [service](https://dstack.ai/docs/services) that deploys
Llama 3.1 8B using
-[Optimum TPU :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://github.com/huggingface/optimum-tpu){:target="_blank"}
-and [vLLM :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://github.com/vllm-project/vllm){:target="_blank"}.
+[Optimum TPU](https://github.com/huggingface/optimum-tpu)
+and [vLLM](https://github.com/vllm-project/vllm).
=== "Optimum TPU"
@@ -79,7 +79,7 @@ and [vLLM :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://github.com/vllm-
```
diff --git a/docs/blog/posts/tpu-on-gcp.md b/docs/blog/posts/tpu-on-gcp.md
index 8fff83cb4..4a45af000 100644
--- a/docs/blog/posts/tpu-on-gcp.md
+++ b/docs/blog/posts/tpu-on-gcp.md
@@ -14,8 +14,8 @@ If you’re using or planning to use TPUs with Google Cloud, you can now do so v
Read below to find out how to use TPUs with `dstack` for fine-tuning and deploying
LLMs, leveraging open-source tools like Hugging Face’s
-[Optimum TPU :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://github.com/huggingface/optimum-tpu){:target="_blank"}
-and [vLLM :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://docs.vllm.ai/en/latest/getting_started/tpu-installation.html){:target="_blank"}.
+[Optimum TPU](https://github.com/huggingface/optimum-tpu)
+and [vLLM](https://docs.vllm.ai/en/latest/getting_started/tpu-installation.html).
@@ -45,8 +45,8 @@ If you've configured the `gcp` backend, `dstack` will automatically provision th
You can use any serving framework, such as vLLM, TGI. Here's an example of a [service](https://dstack.ai/docs/services) that deploys
Llama 3.1 8B using
-[Optimum TPU :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://github.com/huggingface/optimum-tpu){:target="_blank"}
-and [vLLM :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://github.com/vllm-project/vllm){:target="_blank"}.
+[Optimum TPU](https://github.com/huggingface/optimum-tpu)
+and [vLLM](https://github.com/vllm-project/vllm).
=== "Optimum TPU"
@@ -79,7 +79,7 @@ and [vLLM :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://github.com/vllm-
```
@@ -208,12 +208,12 @@ Note, `v5litepod` is optimized for fine-tuning transformer-based models. Each co
## What's next?
-1. Browse [Optimum TPU :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://github.com/huggingface/optimum-tpu){:target="_blank"},
- [Optimum TPU TGI :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://github.com/huggingface/optimum-tpu/tree/main/text-generation-inference){:target="_blank"} and
- [vLLM :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://docs.vllm.ai/en/latest/getting_started/tpu-installation.html){:target="_blank"}.
+1. Browse [Optimum TPU](https://github.com/huggingface/optimum-tpu),
+ [Optimum TPU TGI](https://github.com/huggingface/optimum-tpu/tree/main/text-generation-inference) and
+ [vLLM](https://docs.vllm.ai/en/latest/getting_started/tpu-installation.html).
2. Check [dev environments](../../docs/concepts/dev-environments.md), [tasks](https://dstack.ai/docs/tasks),
[services](../../docs/concepts/services.md), and [fleets](../../docs/concepts/fleets.md).
!!! info "Multi-host TPUs"
If you’d like to use `dstack` with more than eight TPU cores, upvote the corresponding
- [issue :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://github.com/dstackai/dstack/issues/1337){:target="_blank"}.
+ [issue](https://github.com/dstackai/dstack/issues/1337).
diff --git a/docs/docs/concepts/backends.md b/docs/docs/concepts/backends.md
index c89875486..291857139 100644
--- a/docs/docs/concepts/backends.md
+++ b/docs/docs/concepts/backends.md
@@ -10,7 +10,7 @@ They can be configured via `~/.dstack/server/config.yml` or through the [project
* [On-prem](#on-prem) – use `dstack`'s native support for on-prem servers without needing Kubernetes.
!!! info "dstack Sky"
- If you're using [dstack Sky :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://sky.dstack.ai){:target="_blank"}, backend configuration is optional. dstack Sky lets you use pre-configured backends to access GPU marketplace.
+ If you're using [dstack Sky](https://sky.dstack.ai), backend configuration is optional. dstack Sky lets you use pre-configured backends to access GPU marketplace.
See the examples of backend configuration below.
@@ -46,7 +46,7 @@ There are two ways to configure AWS: using an access key or using the default cr
=== "Access key"
- Create an access key by following the [this guide :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://docs.aws.amazon.com/cli/latest/userguide/cli-authentication-user.html#cli-authentication-user-get).
+ Create an access key by following the [this guide](https://docs.aws.amazon.com/cli/latest/userguide/cli-authentication-user.html#cli-authentication-user-get).
Once you've downloaded the `.csv` file with your IAM user's Access key ID and Secret access key, proceed to
configure the backend.
@@ -223,7 +223,7 @@ There are two ways to configure AWS: using an access key or using the default cr
Additionally, private subnets must have outbound internet connectivity provided by NAT Gateway, Transit Gateway, or other mechanism.
??? info "OS images"
- By default, `dstack` uses its own [AMI :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://docs.aws.amazon.com/AWSEC2/latest/UserGuide/AMIs.html)
+ By default, `dstack` uses its own [AMI](https://docs.aws.amazon.com/AWSEC2/latest/UserGuide/AMIs.html)
optimized for `dstack`.
To use your own or other third-party images, set the `os_images` property:
@@ -282,7 +282,7 @@ There are two ways to configure Azure: using a client secret or using the defaul
- If you don't know your `subscription_id` and `tenant_id`, use [Azure CLI :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/cli/azure/install-azure-cli):
+ If you don't know your `subscription_id` and `tenant_id`, use [Azure CLI](https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/cli/azure/install-azure-cli):
```shell
az account show --query "{subscription_id: id, tenant_id: tenantId}"
@@ -290,7 +290,7 @@ There are two ways to configure Azure: using a client secret or using the defaul
=== "Client secret"
- A client secret can be created using the [Azure CLI :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/cli/azure/install-azure-cli):
+ A client secret can be created using the [Azure CLI](https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/cli/azure/install-azure-cli):
```shell
SUBSCRIPTION_ID=...
@@ -320,7 +320,7 @@ There are two ways to configure Azure: using a client secret or using the defaul
 @@ -106,7 +106,7 @@ Here is the spec of the bare metal machine we got:
??? info "TGI"
The `ghcr.io/huggingface/text-generation-inference:sha-11d7af7-rocm` Docker image was used.
-For conducting the tests, we've been using the [`benchmark_serving` :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://github.com/vllm-project/vllm/blob/main/benchmarks/benchmark_serving.py){:target="_blank"} provided by vLLM.
+For conducting the tests, we've been using the [`benchmark_serving`](https://github.com/vllm-project/vllm/blob/main/benchmarks/benchmark_serving.py) provided by vLLM.
## Observations
@@ -175,7 +175,7 @@ to vLLM.
@@ -106,7 +106,7 @@ Here is the spec of the bare metal machine we got:
??? info "TGI"
The `ghcr.io/huggingface/text-generation-inference:sha-11d7af7-rocm` Docker image was used.
-For conducting the tests, we've been using the [`benchmark_serving` :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://github.com/vllm-project/vllm/blob/main/benchmarks/benchmark_serving.py){:target="_blank"} provided by vLLM.
+For conducting the tests, we've been using the [`benchmark_serving`](https://github.com/vllm-project/vllm/blob/main/benchmarks/benchmark_serving.py) provided by vLLM.
## Observations
@@ -175,7 +175,7 @@ to vLLM.
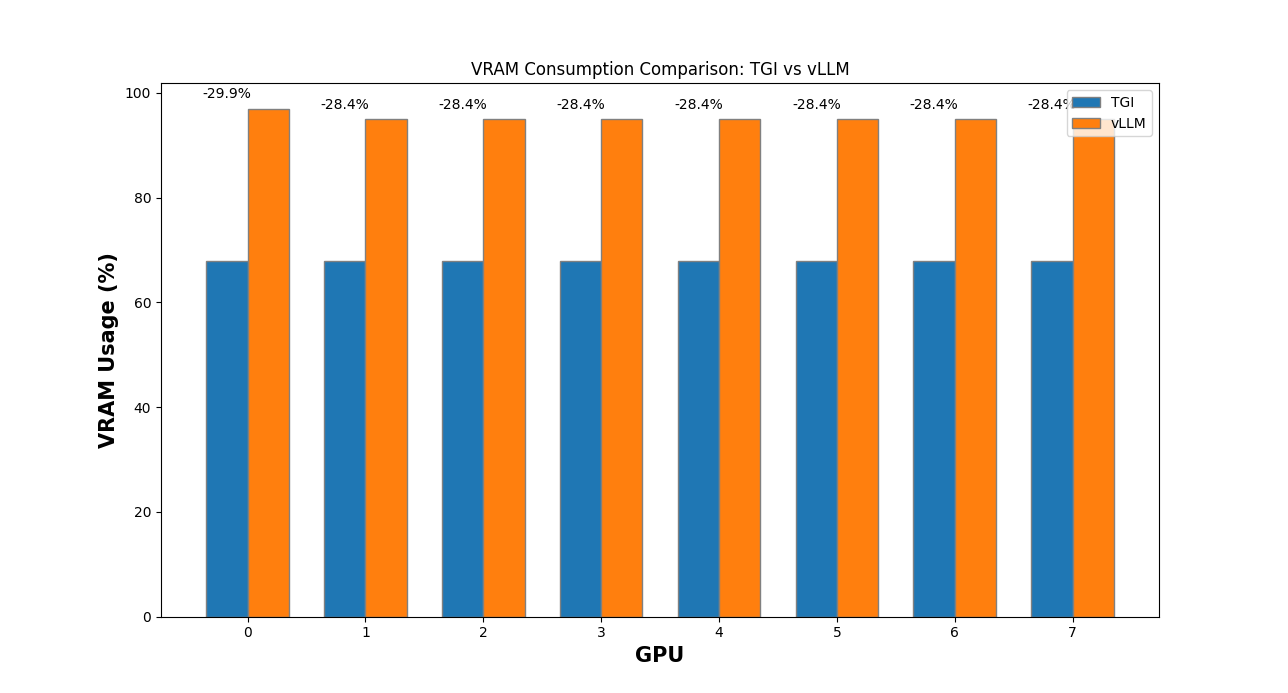 -This difference may be related to how vLLM [pre-allocates GPU cache :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://docs.vllm.ai/en/latest/models/performance.html){:target="_blank"}.
+This difference may be related to how vLLM [pre-allocates GPU cache](https://docs.vllm.ai/en/latest/models/performance.html).
## Conclusion
@@ -203,7 +203,7 @@ like the H100 and H200, as well as possibly Google TPU.
### Source code
The source code used for this benchmark can be found in our
-[GitHub repo :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://github.com/dstackai/benchmarks/tree/main/amd/inference){:target="_blank"}.
+[GitHub repo](https://github.com/dstackai/benchmarks/tree/main/amd/inference).
If you have questions, feedback, or want to help improve the benchmark, please reach out to our team.
@@ -211,7 +211,7 @@ If you have questions, feedback, or want to help improve the benchmark, please r
### Hot Aisle
-[Hot Aisle :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://hotaisle.xyz/){:target="_blank"}
+[Hot Aisle](https://hotaisle.xyz/)
is the primary sponsor of this benchmark, and we are sincerely grateful for their hardware and support.
If you'd like to use top-tier bare metal compute with AMD GPUs, we recommend going
@@ -219,6 +219,6 @@ with Hot Aisle. Once you gain access to a cluster, it can be easily accessed via
### RunPod
If you’d like to use on-demand compute with AMD GPUs at affordable prices, you can configure `dstack` to
-use [RunPod :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://runpod.io/){:target="_blank"}. In
+use [RunPod](https://runpod.io/). In
this case, `dstack` will be able to provision fleets automatically when you run dev environments, tasks, and
services.
diff --git a/docs/blog/posts/amd-on-runpod.md b/docs/blog/posts/amd-on-runpod.md
index 1e32a27e7..c1ff25015 100644
--- a/docs/blog/posts/amd-on-runpod.md
+++ b/docs/blog/posts/amd-on-runpod.md
@@ -33,14 +33,14 @@ One of the main advantages of the `MI300X` is its VRAM. For example, with the `H
version of Llama 3.1 405B into a single node with 8 GPUs—you'd have to use FP8 instead. However, with the `MI300X`, you
can fit FP16 into a single node with 8 GPUs, and for FP8, you'd only need 4 GPUs.
-With the [latest update :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://github.com/dstackai/dstack/releases/0.18.11rc1){:target="_blank"},
+With the [latest update](https://github.com/dstackai/dstack/releases/0.18.11rc1),
you can now specify an AMD GPU under `resources`. Below are a few examples.
## Configuration
=== "Service"
Here's an example of a [service](../../docs/concepts/services.md) that deploys
- Llama 3.1 70B in FP16 using [TGI :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://huggingface.co/docs/text-generation-inference/en/installation_amd){:target="_blank"}.
+ Llama 3.1 70B in FP16 using [TGI](https://huggingface.co/docs/text-generation-inference/en/installation_amd).
-This difference may be related to how vLLM [pre-allocates GPU cache :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://docs.vllm.ai/en/latest/models/performance.html){:target="_blank"}.
+This difference may be related to how vLLM [pre-allocates GPU cache](https://docs.vllm.ai/en/latest/models/performance.html).
## Conclusion
@@ -203,7 +203,7 @@ like the H100 and H200, as well as possibly Google TPU.
### Source code
The source code used for this benchmark can be found in our
-[GitHub repo :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://github.com/dstackai/benchmarks/tree/main/amd/inference){:target="_blank"}.
+[GitHub repo](https://github.com/dstackai/benchmarks/tree/main/amd/inference).
If you have questions, feedback, or want to help improve the benchmark, please reach out to our team.
@@ -211,7 +211,7 @@ If you have questions, feedback, or want to help improve the benchmark, please r
### Hot Aisle
-[Hot Aisle :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://hotaisle.xyz/){:target="_blank"}
+[Hot Aisle](https://hotaisle.xyz/)
is the primary sponsor of this benchmark, and we are sincerely grateful for their hardware and support.
If you'd like to use top-tier bare metal compute with AMD GPUs, we recommend going
@@ -219,6 +219,6 @@ with Hot Aisle. Once you gain access to a cluster, it can be easily accessed via
### RunPod
If you’d like to use on-demand compute with AMD GPUs at affordable prices, you can configure `dstack` to
-use [RunPod :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://runpod.io/){:target="_blank"}. In
+use [RunPod](https://runpod.io/). In
this case, `dstack` will be able to provision fleets automatically when you run dev environments, tasks, and
services.
diff --git a/docs/blog/posts/amd-on-runpod.md b/docs/blog/posts/amd-on-runpod.md
index 1e32a27e7..c1ff25015 100644
--- a/docs/blog/posts/amd-on-runpod.md
+++ b/docs/blog/posts/amd-on-runpod.md
@@ -33,14 +33,14 @@ One of the main advantages of the `MI300X` is its VRAM. For example, with the `H
version of Llama 3.1 405B into a single node with 8 GPUs—you'd have to use FP8 instead. However, with the `MI300X`, you
can fit FP16 into a single node with 8 GPUs, and for FP8, you'd only need 4 GPUs.
-With the [latest update :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://github.com/dstackai/dstack/releases/0.18.11rc1){:target="_blank"},
+With the [latest update](https://github.com/dstackai/dstack/releases/0.18.11rc1),
you can now specify an AMD GPU under `resources`. Below are a few examples.
## Configuration
=== "Service"
Here's an example of a [service](../../docs/concepts/services.md) that deploys
- Llama 3.1 70B in FP16 using [TGI :material-arrow-top-right-thin:{ .external }](https://huggingface.co/docs/text-generation-inference/en/installation_amd){:target="_blank"}.
+ Llama 3.1 70B in FP16 using [TGI](https://huggingface.co/docs/text-generation-inference/en/installation_amd).